In vivo clearance of an intracellular bacterium, Francisella tularensis LVS, is dependent on the p40 subunit of interleukin-12 (IL-12) but not on IL-12 p70
- PMID: 11895957
- PMCID: PMC127864
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.4.1936-1948.2002
In vivo clearance of an intracellular bacterium, Francisella tularensis LVS, is dependent on the p40 subunit of interleukin-12 (IL-12) but not on IL-12 p70
Abstract
To determine the role of interleukin-12 (IL-12) in primary and secondary immunity to a model intracellular bacterium, we have comprehensively evaluated infection with Francisella tularensis LVS in three murine models of IL-12 deficiency. Mice lacking the p40 protein of IL-12 (p40 knockout [KO] mice) and mice treated in vivo with neutralizing anti-IL-12 antibodies survived large doses of primary and secondary LVS infection but never cleared bacteria and exhibited a chronic infection. In dramatic contrast, mice lacking the p35 protein (p35 KO mice) of heterodimeric IL-12 readily survived large doses of primary sublethal LVS infection as well as maximal secondary lethal challenge, with only a slight delay in clearance of bacteria. LVS-immune wild-type (WT) lymphocytes produced large amounts of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), but p35 KO and p40 KO lymphocytes produced much less; nonetheless, similar amounts of NO were found in all cultures containing immune lymphocytes, and all immune lymphocytes were equally capable of controlling intracellular growth of LVS in vitro. Purified CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells from both WT and p40 KO mice controlled intracellular growth, even though T cells from WT mice produced much more IFN-gamma than those from p40 KO mice, and p40 KO T cells did not adopt a Th2 phenotype. Thus, while IL-12 p70 stimulation of IFN-gamma production may be important for bacteriostasis, IL-12 p70 is not necessary for appropriate development of LVS-immune T cells that are capable of controlling intracellular bacterial growth and for clearance of primary or secondary LVS infection. Instead, an additional mechanism dependent on the IL-12 p40 protein, either alone or in another complex such as the newly discovered heterodimer IL-23, appears to be responsible for actual clearance of this intracellular bacterium.
Figures

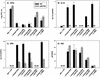
References
-
- Anthony, L. S. D., E. Ghadirian, F. P. Nestel, and P. A. L. Kongshavn. 1989. The requirement for gamma interferon in resistance of mice to experimental tularemia. Microb. Pathog. 7:421-428. - PubMed
-
- Badovinac, V. P., and J. T. Harty. 2000. Adaptive immunity and enhanced CD8+ T cell response to Listeria monocytogenes in the absence of perforin and IFN-gamma. J. Immunol. 164:6444-6452. - PubMed
-
- Brombacher, F., A. Dorfmuller, J. Magram, W. J. Dai, G. Kohler, A. Wunderlin, K. Palmer-Lehmann, M. K. Gately, and G. Alber. 1999. IL-12 is dispensable for innate and adaptive immunity against low doses of Listeria monocytogenes. Int. Immunol. 11:325-332. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

