Stachylysin may be a cause of hemorrhaging in humans exposed to Stachybotrys chartarum
- PMID: 11895972
- PMCID: PMC127818
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.4.2065-2069.2002
Stachylysin may be a cause of hemorrhaging in humans exposed to Stachybotrys chartarum
Abstract
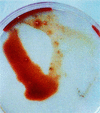
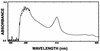
Stachybotrys chartarum is a toxigenic fungus that has been associated with human health concerns such as nasal bleeding in adults and pulmonary hemosiderosis (PH) in infants. Seven of eight strains of S. chartarum isolated from homes of infants with PH in Cleveland, Ohio, and the strain from the lung of an infant with PH in Texas produced stachylysin in tryptic soy broth (TSB), whereas only one out of eight strains isolated from control homes produced stachylysin. However, all strains produced stachylysin when grown on TSB with 0.7% sheep's blood. When stachylysin was injected into Lumbricus terrestis, the erythrocruorin hemoglobin (absorbance peaks at 280 and 415 nm) was released, resulting in a lethal effect. These results support the hypothesis that stachylysin may be one agent responsible for hemorrhaging in humans.
Figures



References
-
- Bhakdi, S., H. Bayley, A. Valeva, I. Walev, B. Walker, U. Weller, M. Kehoe, and M. Palmer. 1996. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin, streptolysin-O, and Escherichia coli hemolysin prototypes of pore-forming bacterial cytolysins. Arch. Microbiol. 165:73-79. - PubMed
-
- Dearborn, D. 1997. Pulmonary hemorrhage in infants and children. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 9:219-224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

