Immunogenicity of a 26-valent group A streptococcal vaccine
- PMID: 11895984
- PMCID: PMC127884
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.4.2171-2177.2002
Immunogenicity of a 26-valent group A streptococcal vaccine
Abstract
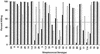
A multivalent vaccine containing amino-terminal M protein fragments from 26 different serotypes of group A streptococci was constructed by recombinant techniques. The vaccine consisted of four different recombinant proteins that were formulated with alum to contain 400 microg of protein per dose. Rabbits were immunized via the intramuscular route at 0, 4, and 16 weeks. Immune sera were assayed for the presence of type-specific antibodies against the individual recombinant M peptides by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and for opsonic antibodies by in vitro opsonization tests and indirect bactericidal tests. The 26-valent vaccine was highly immunogenic and elicited fourfold or greater increases in antibody levels against 25 of the 26 serotypes represented in the vaccine. The immune sera were broadly opsonic and were bactericidal against the majority of the 26 different serotypes. Importantly, none of the immune sera cross-reacted with human tissues. Our results indicate that type-specific, protective M protein epitopes can be incorporated into complex, multivalent vaccines designed to elicit broadly protective opsonic antibodies in the absence of tissue-cross-reactive antibodies.
Figures


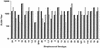
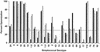
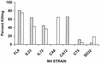
References
-
- Baird, R. W., M. S. Bronze, W. Kraus, H. R. Hill, L. G. Veasey, and J. B. Dale. 1991. Epitopes of group A streptococcal M protein shared with antigens of articular cartilage and synovium. J. Immunol. 146:3132-3137. - PubMed
-
- Beachey, E. H., and J. M. Seyer. 1986. Protective and nonprotective epitopes of chemically synthesized peptides of the NH2-terminal region of type 6 streptococcal M protein. J. Immunol. 136:2287-2292. - PubMed
-
- Beachey, E. H., J. M. Seyer, and J. B. Dale. 1981. Type-specific protective immunity evoked by synthetic peptide of Streptococcus pyogenes M protein. Nature (London) 292:457-459. - PubMed
-
- Beachey, E. H., J. M. Seyer, J. B. Dale, and D. L. Hasty. 1983. Repeating covalent structure and protective immunogenicity of native and synthetic polypeptide fragments of type 24 streptococcal M protein. J. Biol. Chem. 258:13250-13257. - PubMed
-
- Beachey, E. H., J. M. Seyer, and A. H. Kang. 1980. Primary structure of protective antigens of type 24 streptococcal M protein. J. Biol. Chem. 255:6284-6289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

