Balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines correlates with outcome of acute experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis
- PMID: 11895986
- PMCID: PMC127830
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.4.2187-2197.2002
Balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines correlates with outcome of acute experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis
Abstract
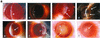
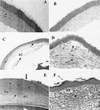
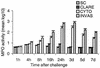
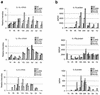
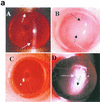
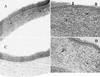
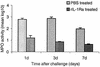
The purpose of this study was to elucidate the expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in mouse corneas infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Three bacterial strains (invasive, cytotoxic, or CLARE [contact lens-induced acute red eye]) which have recently been shown to produce distinct patterns of corneal disease in the mouse were used. The left mouse (BALB/c) corneas were scarified and infected with 2 x 10(6) CFU of one of the three P. aeruginosa strains, while right eyes served as controls. Animals were examined at 1, 4, 8, 16, and 24 h with a slit lamp biomicroscope to grade the severity of infection. Following examination, eyes were collected and processed for histopathology, multiprobe RNase protection assay for cytokine mRNA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to quantitate cytokine proteins, and myeloperoxidase activity to quantitate polymorphonuclear leukocytes. The kinetics of appearance and magnitude of expression of key cytokines varied significantly in the three different phenotypes of P. aeruginosa infection. The predominant cytokines expressed in response to all three phenotypes were interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta), IL-1Ra, and IL-6. In response to the invasive strain, which induced severe corneal inflammation, significantly lower ratios of IL-1Ra to IL-1 beta were present at all time points, whereas corneas challenged with the CLARE strain, which induced very mild inflammation, showed a high ratio of IL-1Ra to IL-1 beta. The outcome of infection in bacterial keratitis correlated with the relative induction of these pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, and exogenous administration of recombinant rIL-1Ra (rIL-1Ra) was able to reduce the disease severity significantly. These findings point to the therapeutic potential of rIL-1Ra protein in possible treatment strategies for bacterial keratitis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of interleukin-6 in the cornea in response to infection with different strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Infect Immun. 1999 May;67(5):2497-502. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.5.2497-2502.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10225913 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17 Promotes Pseudomonas aeruginosa Keratitis in C57BL/6 Mouse Corneas.J Immunol. 2020 Jan 1;204(1):169-179. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900736. Epub 2019 Nov 25. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31767781 Free PMC article.
-
ST2 is essential for Th2 responsiveness and resistance to pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007 Oct;48(10):4626-33. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-0316. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17898286
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and inflammation during contact lens wear: a review.Optom Vis Sci. 2007 Apr;84(4):273-8. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0b013e3180439c3e. Optom Vis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17435510 Review.
-
Role of innate and adaptive immunity in the pathogenesis of keratitis.Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2005 Apr-Jun;13(2-3):133-8. doi: 10.1080/09273940490912362. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2005. PMID: 16019672 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic and transcriptional Profiling of tumor infiltrated CD8+ T cells revealed functional heterogeneity of antitumor immunity in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncoimmunology. 2018 Nov 10;8(2):e1538436. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1538436. eCollection 2019. Oncoimmunology. 2018. PMID: 30713796 Free PMC article.
-
Cathelicidin-deficient (Cnlp -/- ) mice show increased susceptibility to Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007 Oct;48(10):4498-508. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-0274. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17898271 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of Surfactant Protein D in Ocular Staphylococcus aureus Infection.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 23;10(9):e0138597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138597. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26398197 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition by female sex hormones of collagen degradation by corneal fibroblasts.Mol Vis. 2011;17:3415-22. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 22219637 Free PMC article.
-
Predatory bacteria can reduce Pseudomonas aeruginosa induced corneal perforation and proliferation in a rabbit keratitis model.Ocul Surf. 2023 Apr;28:254-261. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2023.05.002. Epub 2023 May 3. Ocul Surf. 2023. PMID: 37146902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira, S., T. Hirano, T. Taga, and T. Kishimoto. 1990. Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF). FASEB J. 4:2860-2867. - PubMed
-
- Amano, S., R. Rohan, and M. Kuroki. 1998. Requirement for VEGF in wound and inflammation related corneal neovascularization. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 39:18-22. - PubMed
-
- Anisowicz, A., M. Messineo, S. W. Lee, and R. Sager. 1991. NF-κB-like transcription factor mediates IL-1/TNF-α induction of GRO in human fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 147:520-527. - PubMed
-
- Baugh, M. D., A. P. Hollander, and G. S. Evans. 1998. The regulation of matrix metalloproteinase production in human colonic fibroblasts. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 859:175-179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

