The neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein is a direct inhibitor of caspases 3 and 7
- PMID: 11896143
- PMCID: PMC6758245
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-06-02035.2002
The neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein is a direct inhibitor of caspases 3 and 7
Abstract
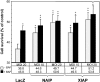
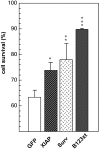
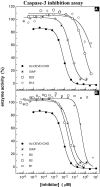
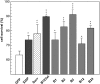
The neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein (NAIP) was identified as a candidate gene for the inherited neurodegenerative disorder spinal muscular atrophy. NAIP is the founding member of a human protein family that is characterized by highly conserved N-terminal motifs called baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis repeats (BIR). Five members of the human family of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins including NAIP have been shown to be antiapoptotic in various systems. To date, a mechanism for the antiapoptotic effect of NAIP has not been elucidated. To investigate NAIP function, we found cytoprotection of NAIP-expressing primary cortical neurons treated to undergo caspase-3-dependent apoptosis. The additional treatment of these neurons with the pancaspase inhibitor boc-aspartyl(OMe)-fluoromethylketone did not result in increased survival. Similar cytoprotective effects were obtained using HeLa cells transiently transfected with a NAIP N-terminal construct and treated to undergo a caspase-3-dependent cell death. To examine whether NAIP inhibits caspases directly, recombinant N-terminal NAIP protein containing BIR domains was overexpressed, purified, and tested for caspase inhibition potential. Our results demonstrate that inhibition of caspases is selective and restricted to the effector group of caspases, with K(i) values as low as approximately 14 nm for caspase-3 and approximately 45 nm for caspase-7. Additional investigations with NAIP fragments containing either one or two NAIP BIRs revealed that the second BIR and to a lesser extent the third BIR alone are sufficient to mediate full caspase inhibition.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Neuronal apoptosis-inhibitory protein does not interact with Smac and requires ATP to bind caspase-9.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 24;279(39):40622-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405963200. Epub 2004 Jul 26. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15280366
-
The neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein suppresses neuronal differentiation and apoptosis in PC12 cells.Hum Mol Genet. 2000 Oct 12;9(17):2479-89. doi: 10.1093/hmg/9.17.2479. Hum Mol Genet. 2000. PMID: 11030753
-
NAIP interacts with hippocalcin and protects neurons against calcium-induced cell death through caspase-3-dependent and -independent pathways.EMBO J. 2000 Jul 17;19(14):3597-607. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.14.3597. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10899114 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection by the inhibition of apoptosis.Brain Pathol. 2000 Apr;10(2):283-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2000.tb00262.x. Brain Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10764048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Involvement of caspase on apoptosis in ischemia-induced neuronal cell death: usefulness of caspase inhibitors for stroke therapy].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1999 Feb;113(2):97-111. doi: 10.1254/fpj.113.97. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1999. PMID: 10205784 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Inhibitor of apoptosis protein-like protein-2 as a novel serological biomarker for breast cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Dec 7;13(12):16737-50. doi: 10.3390/ijms131216737. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23222679 Free PMC article.
-
Critical function for Naip5 in inflammasome activation by a conserved carboxy-terminal domain of flagellin.Nat Immunol. 2008 Oct;9(10):1171-8. doi: 10.1038/ni.1646. Epub 2008 Aug 24. Nat Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18724372 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-radiation (GR) triggers a unique gene expression profile associated with cell death compared to proton radiation (PR) in mice in vivo.Cancer Biol Ther. 2008 Dec;7(12):2023-33. doi: 10.4161/cbt.7.12.7417. Epub 2008 Dec 17. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008. PMID: 19106632 Free PMC article.
-
Survivin and NAIP in Human Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Protective Role of the Association of Serenoa repens, Lycopene and Selenium from the Randomized Clinical Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Mar 22;18(3):680. doi: 10.3390/ijms18030680. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28327526 Free PMC article.
-
The synergistic effect of Mig-6 and Pten ablation on endometrial cancer development and progression.Oncogene. 2010 Jul 1;29(26):3770-80. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.126. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20418913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chai J, Shiozaki E, Srinivasula SM, Wu Q, Dataa P, Alnemri ES, Shi Y. Structural basis of caspase-7 inhibition by XIAP. Cell. 2001;104:769–780. - PubMed
-
- Cheng Y, Prusoff WH. Relationship between the inhibition constant (Ki) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 percent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973;22:3099–3108. - PubMed
-
- Cotman CW. Apoptosis decision cascades and neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1998;19:S29–S32. - PubMed
-
- Deveraux QL, Reed JC. IAP family proteins—suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999;3:239–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
