Synaptically released glutamate activates extrasynaptic NMDA receptors on cells in the ganglion cell layer of rat retina
- PMID: 11896156
- PMCID: PMC6758274
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-06-02165.2002
Synaptically released glutamate activates extrasynaptic NMDA receptors on cells in the ganglion cell layer of rat retina
Abstract
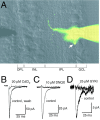
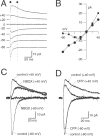
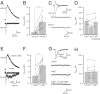
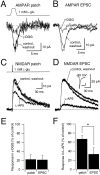
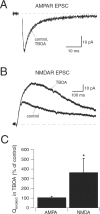
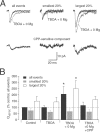
NMDA and AMPA receptors (NMDARs and AMPARs) are colocalized at most excitatory synapses in the CNS. Consequently, both receptor types are activated by a single quantum of transmitter and contribute to miniature and evoked EPSCs. However, in amphibian retina, miniature EPSCs in ganglion cell layer neurons are mediated solely by AMPARs, although both NMDARs and AMPARs are activated during evoked EPSCs. One explanation for this discrepancy is that NMDARs are located outside of the synaptic cleft and are activated only when extrasynaptic glutamate levels increase during coincident release from multiple synapses. Alternatively, NMDARs may be segregated at synapses that either are not spontaneously active or yield miniature EPSCs that are too small to detect. In this study, we examined excitatory, glutamatergic synaptic inputs to neurons in the ganglion cell layer of acute slices of rat retina. EPSCs, elicited by electrically stimulating presynaptic bipolar cells, exhibited both NMDAR- and AMPAR-mediated components. However, spontaneous EPSCs exhibited only an AMPAR-mediated component. The effects of low-affinity, competitive receptor antagonists indicated that NMDARs encounter less glutamate than AMPARs during an evoked synaptic response. Reducing glutamate uptake or changing the probability of release preferentially affected the NMDAR component in evoked EPSCs; reducing uptake revealed an NMDAR component in spontaneous EPSCs. These results indicate that NMDARs are located extrasynaptically and that glutamate transporters prevent NMDAR activation by a transmitter released from a single vesicle and limit their activation during evoked responses.
Figures

References
-
- Asztely F, Erdemli G, Kullmann DM. Extrasynaptic glutamate spillover in the hippocampus: dependence on temperature and the role of active glutamate uptake. Neuron. 1997;18:281–293. - PubMed
-
- Bekkers JM, Stevens CF. NMDA and non-NMDA receptors are co-localized at individual excitatory synapses in cultured rat hippocampus. Nature. 1989;341:230–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
