Epidemiology of Burkholderia cepacia complex in patients with cystic fibrosis, Canada
- PMID: 11897071
- PMCID: PMC3369581
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0802.010163
Epidemiology of Burkholderia cepacia complex in patients with cystic fibrosis, Canada
Abstract
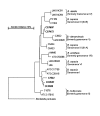
The Burkholderia cepacia complex is an important group of pathogens in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF). Although evidence for patient-to-patient spread is clear, microbial factors facilitating transmission are poorly understood. To identify microbial clones with enhanced transmissibility, we evaluated B. cepacia complex isolates from patients with CF from throughout Canada. A total of 905 isolates from the B. cepacia complex were recovered from 447 patients in 8 of the 10 provinces; 369 (83%) of these patients had genomovar III and 43 (9.6%) had B. multivorans (genomovar II). Infection prevalence differed substantially by region (22% of patients in Ontario vs. 5% in Quebec). Results of typing by random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis or pulsed-field gel electrophoresis indicated that strains of B. cepacia complex from genomovar III are the most potentially transmissible and that the B. cepacia epidemic strain marker is a robust marker for transmissibility.
Figures
References
-
- Speert DP, Bond M, Woodman RC, Curnutte JT. Infection with Pseudomonas cepacia in chronic granulomatous disease: role of nonoxidative killing by neutrophils in host defense. J Infect Dis. 1994;170:1524–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
