Oxazolidinone antibiotics target the P site on Escherichia coli ribosomes
- PMID: 11897593
- PMCID: PMC127084
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.4.1080-1085.2002
Oxazolidinone antibiotics target the P site on Escherichia coli ribosomes
Abstract
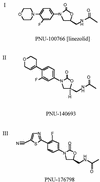
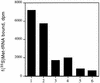
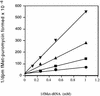
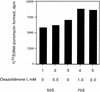
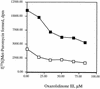
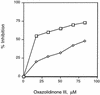
The oxazolidinones are a novel class of antimicrobial agents that target protein synthesis in a wide spectrum of gram-positive and anaerobic bacteria. The oxazolidinone PNU-100766 (linezolid) inhibits the binding of fMet-tRNA to 70S ribosomes. Mutations to oxazolidinone resistance in Halobacterium halobium, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli map at or near domain V of the 23S rRNA, suggesting that the oxazolidinones may target the peptidyl transferase region responsible for binding fMet-tRNA. This study demonstrates that the potency of oxazolidinones corresponds to increased inhibition of fMet-tRNA binding. The inhibition of fMet-tRNA binding is competitive with respect to the fMet-tRNA concentration, suggesting that the P site is affected. The fMet-tRNA reacts with puromycin to form peptide bonds in the presence of elongation factor P (EF-P), which is needed for optimum specificity and efficiency of peptide bond synthesis. Oxazolidinone inhibition of the P site was evaluated by first binding fMet-tRNA to the A site, followed by translocation to the P site with EF-G. All three of the oxazolidinones used in this study inhibited translocation of fMet-tRNA. We propose that the oxazolidinones target the ribosomal P site and pleiotropically affect fMet-tRNA binding, EF-P stimulated synthesis of peptide bonds, and, most markedly, EF-G-mediated translocation of fMet-tRNA into the P site.
Figures

References
-
- Aoki, H., S.-L. Adams, M. A. Turner, and M. C. Ganoza. 1997. Molecular characterization of the efp gene product involved in a peptidyl transferase reaction. Biochimie 79:7-11. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. Rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
-
- Brickner, S. J., M. R. Hutchinson, M. R. Barbachyn, P. R. Manninen, D. A. Ulaniwicz, S. A. Garmon, K. C. Grega, S. K. Hendges, D. S. Toops, C. W. Ford, and G. E. Zurenko. 1996. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of U-100592 and U-100766, two oxazolidinone antibacterial agents for the potential treatment of multidrug-resistant gram-positive bacterial infections. J. Med. Chem. 39:673-679. - PubMed
-
- Chung D.-G., N. D. Zahib, R. M. Baxter, and M. C. Ganoza. 1990. Peptidyl transferase: the soluble protein EFP restores the efficiency of 70S ribosome catalyzed peptide bond synthesis, p. 69-80. In G. Spedding (ed.), Ribosomes and protein synthesis: a practical approach. IRL Press, Oxford Publishing Co., Oxford, United Kingdom.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

