Plk1 promotes nuclear translocation of human Cdc25C during prophase
- PMID: 11897663
- PMCID: PMC1084057
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf069
Plk1 promotes nuclear translocation of human Cdc25C during prophase
Abstract
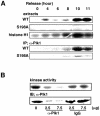
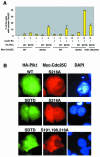
The nuclear accumulation of active M-phase promoting factor (MPF) during prophase is thought to be essential for coordinating M-phase events in vertebrate cells. The protein phosphatase Cdc25C, an activator of MPF, enters the nucleus to keep MPF active in the nucleus during prophase. However, the molecular mechanisms that control nuclear translocation of Cdc25C during prophase are unknown. We show that phosphorylation of a serine residue (Ser198) in a nuclear export signal sequence of human Cdc25C occurs during prophase and promotes nuclear localization of Cdc25C. We also show that Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) is responsible for this phosphorylation and that constitutively active Plk1 promotes nuclear localization of Cdc25C. Remarkably, a mutant Cdc25C in which Ser198 is replaced by alanine remains in the cytoplasm when wild-type Cdc25C accumulates in the nucleus during prophase. These results suggest that Plk1 phosphorylates Cdc25C on Ser198 and regulates nuclear translocation of Cdc25C during prophase.
Figures




References
-
- Blasina A., Van de Weyer, M., Laus, M.C., Luyten, W.H., Parker, A.E. and McGowan, C.H. (1999) A human homologue of the checkpoint kinase Cds1 directly inhibits Cdc25 phosphatase. Curr. Biol., 9, 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Coleman T.R. and Dunphy, W.G. (1994) Cdc2 regulatory factors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 6, 877–882. - PubMed
-
- Furnari B., Rhind, N. and Russell, P. (1997) Cdc25 mitotic inducer targeted by chk1 DNA damage checkpoint kinase. Science, 277, 1450–1451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

