Functional differences between alpha subunit isoforms of the rat Na,K-ATPase expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- PMID: 11897839
- PMCID: PMC2290179
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013201
Functional differences between alpha subunit isoforms of the rat Na,K-ATPase expressed in Xenopus oocytes
Abstract
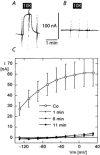
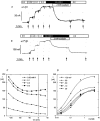
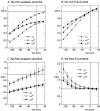
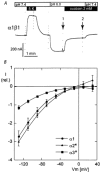
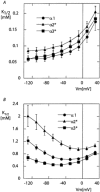
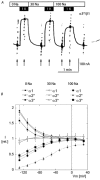
The functional properties of the three most widely distributed alpha subunit isoforms of the Na,K-ATPase are not well known, particularly concerning the voltage dependence of their activity and cation binding kinetics. We measured the electrogenic activity generated by Na,K-ATPases resulting from co-expression of the rat alpha1, alpha2* or alpha3* subunits with the rat beta1 subunit in Xenopus oocytes; alpha2* and alpha3* are ouabain-resistant mutants of the alpha2 and alpha3 isoform, which allowed selective inhibition of the endogenous Na(+),K(+)-pump of the oocyte. In oocytes expressing the three isoforms of the alpha subunit, K(+) induced robust outward currents that were largely ouabain-sensitive. In addition, ouabain-sensitive inward currents were recorded for all three isoforms in sodium-free and potassium-free acid solutions. The very similar voltage dependence of the Na(+),K(+)-pump activity observed in the absence of extracellular Na(+) indicated a similar stoichiometry of the transported cations by the three isoforms. The affinity for extracellular K(+) was slightly lower for the alpha2* and alpha3* than for the alpha1 isoform. The alpha2* isoform was, however, more sensitive to voltage-dependent inhibition by extracellular Na(+), indicating a higher affinity of the extracellular Na(+) site in this isoform. We measured and controlled [Na(+)](i) using a co-expressed amiloride-sensitive Na(+) channel. The intracellular affinity for Na(+) was slightly higher in the alpha2* than in the alpha1 or alpha3* isoforms. These results suggest that the alpha2 isoform could have an activity that is strongly dependent upon [Na(+)](o) and [K(+)](o). These concentrations could selectively modulate its activity when large variations are present, for instance in the narrow intercellular spaces of brain or muscle tissues.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA from heart of young and old rats leads to the expression of protein(s) in Xenopus oocytes that alter the transport activity of rat Na+,K+-ATPases differently.Pflugers Arch. 2001 Oct;443(1):84-91. doi: 10.1007/s004240100662. Pflugers Arch. 2001. PMID: 11692271
-
Glutamate transporter activity promotes enhanced Na+ /K+ -ATPase-mediated extracellular K+ management during neuronal activity.J Physiol. 2016 Nov 15;594(22):6627-6641. doi: 10.1113/JP272531. Epub 2016 Jun 29. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27231201 Free PMC article.
-
Transport and pharmacological properties of nine different human Na, K-ATPase isozymes.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jan 21;275(3):1976-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.3.1976. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10636900
-
The cardiac sodium pump: structure and function.Basic Res Cardiol. 2002;97 Suppl 1:I19-24. doi: 10.1007/s003950200024. Basic Res Cardiol. 2002. PMID: 12479229 Review.
-
[Molecular and functional diversity of NA,K-ATPase and renal H,K-ATPases].Nephrologie. 1996;17(7):401-8. Nephrologie. 1996. PMID: 9019667 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The structure of the Na+,K+-ATPase and mapping of isoform differences and disease-related mutations.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009 Jan 27;364(1514):217-27. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0201. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 18957371 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related changes in Na, K-ATPase expression, subunit isoform selection and assembly in the stria vascularis lateral wall of mouse cochlea.Hear Res. 2018 Sep;367:59-73. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2018.07.006. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Hear Res. 2018. PMID: 30029086 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of the Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase, NKCC1, and Kir4.1 to hippocampal K⁺ clearance and volume responses.Glia. 2014 Apr;62(4):608-22. doi: 10.1002/glia.22629. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Glia. 2014. PMID: 24482245 Free PMC article.
-
Role of homologous ASP334 and GLU319 in human non-gastric H,K- and Na,K-ATPases in cardiac glycoside binding.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Apr 27;356(1):142-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.02.119. Epub 2007 Mar 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17349614 Free PMC article.
-
The Critical Role of Spreading Depolarizations in Early Brain Injury: Consensus and Contention.Neurocrit Care. 2022 Jun;37(Suppl 1):83-101. doi: 10.1007/s12028-021-01431-w. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Neurocrit Care. 2022. PMID: 35257321 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Apell H-J, Karlish SJ. Functional properties of Na,K-ATPase, and their structural implications, as detected with biophysical techniques. Journal of Membrane Biology. 2001;180:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Argüello JM, Peluffo RD, Feng JN, Lingrel JB, Berlin JR. Substitution of glutamic 779 with alanine in the Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit removes voltage dependence of ion transport. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996;271:24610–24616. - PubMed
-
- Blanco G, Mercer RW. Isozymes of the Na-K-ATPase: Heterogeneity in structure, diversity in function. American Journal of Physiology. 1998;44:F633–F650. - PubMed
-
- Blostein R. Proton-activated rubidium transport catalyzed by the sodium pump. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1985;260:829–833. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

