Selective reduction by dopamine of excitatory synaptic inputs to pyramidal neurons in primate prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 11897842
- PMCID: PMC2290171
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.015024
Selective reduction by dopamine of excitatory synaptic inputs to pyramidal neurons in primate prefrontal cortex
Abstract
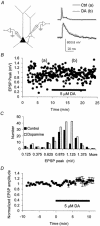
We have employed in vitro physiological methods to investigate dopaminergic modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission in monkey prefrontal cortex (PFC) circuits. We show that combined activation of D1-like and D2-like dopamine receptors results in the reduction of extracellular stimulation-evoked isolated EPSCs in layer 3 pyramidal neurons. Using paired recordings from synaptically connected pyramidal neurons we have determined the basic properties of unitary synaptic connections between layer 3 pyramids in the primate PFC and, interestingly, we found that dopamine does not reduce synaptic transmission between nearby pairs of synaptically coupled PFC pyramidal neurons. This input specificity may be a critical aspect of the dopaminergic regulation of recurrent excitatory circuits in the PFC.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dopamine enhances EPSCs in layer II-III pyramidal neurons in rat prefrontal cortex.J Neurosci. 2003 Feb 1;23(3):867-75. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-03-00867.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12574415 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D1 and D4 receptor subtypes differentially modulate recurrent excitatory synapses in prefrontal cortical pyramidal neurons.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 Feb;31(2):318-38. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300829. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006. PMID: 16052247
-
Layer-specific effects of dopaminergic D1 receptor activation on excitatory synaptic trains in layer V mouse prefrontal cortical pyramidal cells.Physiol Rep. 2018 Aug;6(15):e13806. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13806. Physiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30073790 Free PMC article.
-
Prefrontal dopamine in associative learning and memory.Neuroscience. 2014 Dec 12;282:217-29. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.09.026. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 25241063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine neurotransmission and atypical antipsychotics in prefrontal cortex: a critical review.Curr Top Med Chem. 2012;12(21):2357-74. doi: 10.2174/156802612805289872. Curr Top Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 23279176 Review.
Cited by
-
Dopamine and corticotropin-releasing factor synergistically alter basolateral amygdala-to-medial prefrontal cortex synaptic transmission: functional switch after chronic cocaine administration.J Neurosci. 2008 Jan 9;28(2):529-42. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2666-07.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18184795 Free PMC article.
-
Higher dopamine D1 receptor expression in prefrontal parvalbumin neurons underlies higher distractibility in marmosets versus macaques.Commun Biol. 2025 Jul 1;8(1):974. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-08297-0. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40594842 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of dopamine-directed treatments on cognition.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015 Jul 29;11:1859-75. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S65875. eCollection 2015. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015. PMID: 26251602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of columnar and laminar cognitive processing in primate prefrontal cortex following cocaine exposure.Front Syst Neurosci. 2015 May 29;9:79. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2015.00079. eCollection 2015. Front Syst Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26074787 Free PMC article.
-
Layer- and Cell Type-Specific Modulation of Excitatory Neuronal Activity in the Neocortex.Front Neuroanat. 2018 Jan 30;12:1. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2018.00001. eCollection 2018. Front Neuroanat. 2018. PMID: 29440997 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berger B, Gaspar P, Verney C. Dopaminergic innervation of the cerebral cortex: unexpected differences between rodents and primates. Trends in Neurosciences. 1991;14:21–27. - PubMed
-
- Brozoski TJ, Brown RM, Rosvold HE, Goldman PS. Cognitive deficit caused by regional depletion of dopamine in prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkey. Science. 1979;205:929–932. - PubMed
-
- Camperi M, Wang XJ. A model of visuospatial working memory in prefrontal cortex: recurrent network and cellular bistability. Journal of Computational Neuroscience. 1998;5:383–405. - PubMed
-
- Durstewitz D, Seamans JK, Sejnowski TJ. Neurocomputational models of working memory. Nature Neuroscience. 2000;3:1184–1191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

