MgATP counteracts intracellular proton inhibition of the sodium-calcium exchanger in dialysed squid axons
- PMID: 11897850
- PMCID: PMC2290192
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013377
MgATP counteracts intracellular proton inhibition of the sodium-calcium exchanger in dialysed squid axons
Abstract
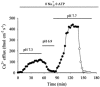
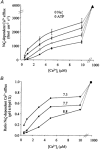
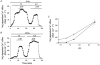
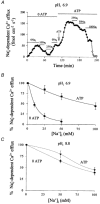
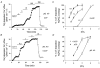
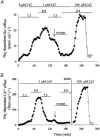
Intracellular Na(+) and H(+) inhibit Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchange. ATP regulates exchange activity by altering kinetic parameters for Ca(2+)(i), Na(+)(i) and Na(+)(o). The role of the Ca(2+)(i)regulatory site on Na(+)(i)-H(+)(i)-ATP interactions was explored by measuring the Na(+)(o)-dependent (45)Ca(2+) efflux (Na(+)(o)-Ca(2+)(i) exchange) and Ca(2+)(i)-dependent (22)Na(+) efflux (Na(+)(o)-Na(+)(i) exchange) in intracellular-dialysed squid axons. Our results show that: (1) without ATP, inhibition by Na(+)(i) is strongly dependent on H(+)(i). Lowering the pH(i) by 0.4 units from its physiological value of 7.3 causes 80 % inhibition of Na(+)(o)-Ca(2+)(i) exchange; (2) in the presence of MgATP, H(+)(i) and Na(+)(i) inhibition is markedly diminished; and (3) experiments on Na(+)(o)-Na(+)(i) exchange indicate that the drastic changes in the Na(+)(i)-H(+)(i)-ATP interactions take place at the Ca(2+)(i) regulatory site. The increase in Ca(2+)(i) affinity induced by ATP at acid pH (6.9) can be mimicked by a rise in pH(i) from 6.9 to 7.3 in the absence of the nucleotide. We conclude that ATP modulation of the Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchange occurs by protection from intracellular proton and sodium inhibition. These findings are predicted by a model where: (i) the binding of Ca(2+) to the regulatory site is essential for translocation but not for the binding of Na(+)(i) or Ca(2+)(i) to the transporting site; (ii) H(+)(i) competes with Ca(2+)(i) for the same form of the exchanger without an effect on the Ca(2+)(i) transporting site; (iii) protonation of the carrier increases the apparent affinity and changes the cooperativity for Na(+)(i) binding; and (iv) ATP prevents both H(+)(i) and Na(+)(i)-effects. The relief of H(+) and Na(+) inhibition induced by ATP could be important in cardiac ischaemia, in which a combination of acidosis and rise in [Na(+)](i) occurs.
Figures
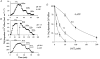
Similar articles
-
Differential up-regulation of Na+-Ca2+ exchange by phosphoarginine and ATP in dialysed squid axons.J Physiol. 1998 Mar 15;507 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):737-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.737bs.x. J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9508835 Free PMC article.
-
In dialyzed squid axons oxidative stress inhibits the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger by impairing the Cai2+-regulatory site.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Sep;301(3):C687-94. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00521.2010. Epub 2011 Jun 1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21633079
-
Intracellular ionic and metabolic regulation of squid nerve Na+/Ca2+ exchanger.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Nov;976:224-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04745.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. PMID: 12502565
-
Ionic ligand interactions with the intracellular loop of the sodium-calcium exchanger. Modulation by ATP.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2002 Jul-Aug;80(1-2):43-67. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6107(02)00014-7. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12231222 Review.
-
The squid preparation as a general model for ionic and metabolic Na+/Ca2+ exchange interactions: physiopathological implications.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Mar;1099:135-51. doi: 10.1196/annals.1387.049. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17446451 Review.
Cited by
-
In the squid axon Na+/Ca2+ exchanger the state of the Ca i-regulatory site influences the affinities of the intra- and extracellular transport sites for Na+ and Ca2+.Pflugers Arch. 2008 Jun;456(3):623-33. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0430-0. Epub 2008 Jan 3. Pflugers Arch. 2008. PMID: 18172600
-
Phosphoarginine regulation of the squid nerve Na+/Ca2+ exchanger: metabolic pathway and exchanger-ligand interactions different from those seen with ATP.J Physiol. 2004 Jan 15;554(Pt 2):387-401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.050930. Epub 2003 Oct 24. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14578490 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asteggiano C, Berberián G, Beaugé L. Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate bound to bovine cardiac Na/Ca exchanger displays a MgATP regulation similar to that of the exchange fluxes. European Journal of Biochemistry. 2001;268:437–442. - PubMed
-
- Baker PF, McNaughton PA. Selective inhibition of the Ca-dependent Na efflux from intact squid axons by a fall in intracellular pH. Journal of Physiology. 1977;269:78P–79P. - PubMed
-
- Berberián G, Hidalgo C, DiPolo R, Beaugé L. ATP stimulation of Na+/Ca2+ exchange in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. American Journal of Physiology. 1998;274:C724–C733. - PubMed
-
- Blaustein MP, Lederer WJ. Sodium/calcium exchange: its physiological implications. Physiological Reviews. 1999;79:763–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

