Interleukin-1 beta, but not interleukin-1 alpha, is required for T-cell-dependent antibody production
- PMID: 11899425
- PMCID: PMC1783318
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2001.01337.x
Interleukin-1 beta, but not interleukin-1 alpha, is required for T-cell-dependent antibody production
Abstract
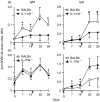
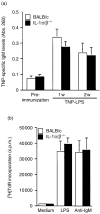
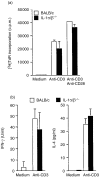
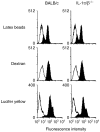
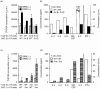
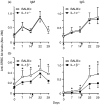
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) consists of two molecules, IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta, and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) is a natural inhibitor of these molecules. Although the adjuvant effects of exogenously administered IL-1 in the humoral immune response are well known, the roles of endogenous IL-1 and the functional discrimination between IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta have not been elucidated completely. In this report, we investigated the role of IL-1 in the humoral immune response using gene-targeted mice. Both primary and secondary antibody production against T-dependent antigen, sheep red blood cells (SRBC), was significantly reduced in IL-1 alpha/beta-/- mice, and was enhanced in IL-1Ra-/- mice. The intrinsic functions of B cells, such as antibody production against type 1 T-independent antigen, trinitrophenyl-lipopolysaccharide and proliferative responses against mitogenic stimuli, were normal in IL-1 alpha/beta-/- mice. The proliferative response of T cells and cytokine production upon stimulation with anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody were also normal, as was the phagocytotic ability of antigen-presenting cells (APCs). However, SRBC-specific proliferative response and cytokine production of T cells through the interaction with APCs were markedly impaired in IL-1 alpha/beta-/- mice, and enhanced in IL-1Ra-/- mice. Moreover, we show that SRBC-specific antibody production was reduced in IL-1 beta-/- mice, but not in IL-1 alpha-/- mice. These results show that endogenous IL-1 beta, but not IL-1 alpha, is involved in T-cell-dependent antibody production, and IL-1 promotes the antigen-specific T-cell helper function through the T-cell-APC interaction.
Figures
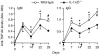
Similar articles
-
Immunoregulation in the rat: cellular and molecular requirements for B cell responses to types 1, 2, and T-dependent antigens.J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2236-46. J Immunol. 1985. PMID: 2857748
-
Anti-4-1BB monoclonal antibodies abrogate T cell-dependent humoral immune responses in vivo through the induction of helper T cell anergy.J Exp Med. 1999 Nov 15;190(10):1535-40. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.10.1535. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 10562327 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1 enhances T cell-dependent antibody production through induction of CD40 ligand and OX40 on T cells.J Immunol. 2001 Jul 1;167(1):90-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.1.90. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11418636
-
Aberrant T-cell function in vitro and impaired T-cell dependent antibody response in vivo in vitamin A-deficient rats.Immunology. 1993 Dec;80(4):581-6. Immunology. 1993. PMID: 8307607 Free PMC article.
-
How many T cells help one B cell?Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1980 May;3(1):129-44. doi: 10.1007/BF00199928. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1980. PMID: 6792725 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-1 as Innate Mediator of T Cell Immunity.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 27;11:621931. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.621931. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33584721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of the Itaconate Pathway Attenuates Murine Lupus.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022 Dec;74(12):1971-1983. doi: 10.1002/art.42284. Epub 2022 Nov 6. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35791960 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of carbohydrate moiety structure on the immunoregulatory activity of lactoferrin in vitro.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2014 Jun;19(2):284-96. doi: 10.2478/s11658-014-0196-2. Epub 2014 May 12. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24820230 Free PMC article.
-
Dual functionality of interleukin-1 family cytokines: implications for anti-interleukin-1 therapy.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Aug;157(8):1318-29. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00331.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19681864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homeostatic regulation of T follicular helper and antibody response to particle antigens by IL-1Ra of medullary sinus macrophage origin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Apr 27;118(17):e2019798118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2019798118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33875594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dinarello CA. Biologic basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood. 1996;87:2095–147. - PubMed
-
- Tocci MJ, Schmidt JA. Interleukin-1: Structure and Function. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1997. Cytokines in Health and Disease; pp. 1–27.
-
- Dinarello CA. Interleukin-1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997;8:253–65. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991;77:1627–52. - PubMed
-
- Falk W, Mannel DN, Darjes H, Krammer PH. IL-1 induces high affinity IL-2 receptor expression of CD4−8− thymocytes. J Immunol. 1989;143:513–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

