Adrenaline suppression of the macrophage nitric oxide response to lipopolysaccharide is associated with differential regulation of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-10
- PMID: 11899430
- PMCID: PMC1783325
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2001.01332.x
Adrenaline suppression of the macrophage nitric oxide response to lipopolysaccharide is associated with differential regulation of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-10
Abstract
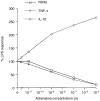
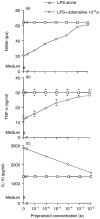
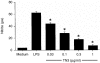
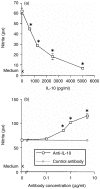
Adrenaline is a catecholamine hormone secreted by the adrenal medulla in response to acute stress. Previous studies have shown that adrenaline suppresses the nitric oxide (NO) response of murine macrophages (M phi s) stimulated in vitro with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). We have now extended these studies to examine the effects of adrenaline on the production of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-10 (IL-10). Our results showed that NO, TNF-alpha and IL-10 were concurrently produced following in vitro LPS (10 micrograms/ml) stimulation of murine peritoneal M phi s. Adrenaline suppressed both NO and TNF-alpha with concomitant up-regulation of the IL-10 response above that seen with LPS alone. In this in vitro model of LPS stimulation we demonstrated that TNF-alpha was required for NO production, as the TNF-alpha neutralizing monoclonal antibody, TN3.19.12, abolished the response; in contrast, IL-10 suppressed NO. In order to determine any functional consequence of adrenaline-mediated IL-10 augmentation on NO production, M phi s were stimulated with LPS and specific neutralizing anti-IL-10 antibodies were added to the cultures. The LPS NO response was suppressed to 43% of the control value by adrenaline (10(-8) M) and an irrelevant control antibody had no effect on the adrenaline-mediated inhibition of NO, but anti-IL-10 treatment restored the NO response to levels similar to those observed with LPS alone. Furthermore, we demonstrated that exogenous TNF-alpha, at a dose range of 1.9-50 ng per ml, also restored the nitrite response to LPS in the presence of adrenaline. Together, the observations that neutralization of IL-10 and addition of TNF-alpha abrogate adrenaline's inhibition of NO, suggest that this hormone suppresses NO partly through up-regulation of IL-10 which, in turn, may suppress TNF-alpha that is required for NO production. Finally, we also observed that the M phi-activating cytokine, interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), attenuated the inhibitory effect of adrenaline on the LPS NO response.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activated peritoneal macrophages inhibit the proliferation of rat ascites hepatoma AH-130 cells via the production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and nitric oxide.Inflamm Res. 2000 Oct;49(10):541-7. doi: 10.1007/s000110050629. Inflamm Res. 2000. PMID: 11089907
-
Adrenaline inhibits macrophage nitric oxide production through beta1 and beta2 adrenergic receptors.Immunology. 2000 Jul;100(3):359-63. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00029.x. Immunology. 2000. PMID: 10929058 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for the involvement of interleukin 10 in the differential deactivation of murine peritoneal macrophages by prostaglandin E2.J Exp Med. 1994 Dec 1;180(6):2365-70. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.6.2365. J Exp Med. 1994. PMID: 7525853 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of nitric oxide synthesis in infectious and autoimmune diseases.Immunol Lett. 1994 Dec;43(1-2):95-8. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(94)00157-x. Immunol Lett. 1994. PMID: 7737695 Review.
-
Review of the macrophage disappearance reaction.J Leukoc Biol. 1995 Mar;57(3):361-7. doi: 10.1002/jlb.57.3.361. J Leukoc Biol. 1995. PMID: 7884305 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of β-Adrenergic Receptors in the Regulation of the Functions of Innate Immune Cells during Cold Stress In Vivo.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2022 May;173(1):72-76. doi: 10.1007/s10517-022-05496-1. Epub 2022 May 26. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35616789
-
TNFα-Mediated Necroptosis Aggravates Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in the Fatty Liver by Regulating the Inflammatory Response.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 May 12;2019:2301903. doi: 10.1155/2019/2301903. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31214277 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosenescence and macrophage functional plasticity: dysregulation of macrophage function by age-associated microenvironmental changes.Immunol Rev. 2005 Jun;205:60-71. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00260.x. Immunol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15882345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epinephrine is associated with both erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms.Fertil Steril. 2010 Feb;93(3):837-42. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.10.034. Epub 2008 Dec 4. Fertil Steril. 2010. PMID: 19062003 Free PMC article.
-
Exhaustive exercise reduces TNF-α and IFN-α production in response to R-848 via toll-like receptor 7 in mice.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010 Nov;110(4):797-803. doi: 10.1007/s00421-010-1560-1. Epub 2010 Jul 3. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20602110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wei X, Charles IG, Smith A, et al. Altered immune response in mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthetase. Nature. 1995;375:408–11. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B, Milsark IW, Cerami AC. Passive immunisation against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effects of endotoxin. Science. 1985;229:869–71. - PubMed
-
- Casey LC, Balk RA, Bone RC. Plasma cytokine and endotoxin levels correlate with survival in patients with the sepsis syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1993;119:771–8. - PubMed
-
- Wysocka M, Kubin M, Vieira LQ, Ozmen L, Garotta G, Scott P, Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12 is required for interferon-γ production and lethality in lipopolysaccharide-induced shock in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1995;25:672–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

