Nitric oxide-enhanced resistance to oral candidiasis
- PMID: 11899431
- PMCID: PMC1783321
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2001.01331.x
Nitric oxide-enhanced resistance to oral candidiasis
Abstract
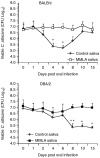
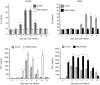
A murine model of oral candidiasis was used to show that nitric oxide (NO) is involved in host resistance to infection with Candida albicans in infection-'resistant' BALB/c and infection-'prone' DBA/2 mice. Following infection, increased NO production was detected in saliva. Postinfection samples of saliva inhibited the growth of yeast in vitro. Treatment with NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (MMLA), an inhibitor of NO synthesis, led to reduced NO production, which correlated with an increase in C. albicans growth. Reduction in NO production following MMLA treatment correlated with an abrogation of interleukin-4 (IL-4), but not interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), mRNA gene expression in regional lymph node cells. Down-regulation of IL-4 production was accompanied with an increase in IFN-gamma production in infection-'prone' DBA/2 mice. There was a functional relationship between IL-4 and NO production in that mice treated with anti-IL-4 monoclonal antibody showed a marked inhibition of NO production in saliva and in culture of cervical lymph node cells stimulated with C. albicans antigen. The results support previous conclusions that IL-4 is associated with resistance to oral candidiasis and suggest that NO is involved in controlling colonization of the oral mucosal surface with C. albicans.
Figures


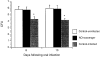


References
-
- Bodey GP. Infection in cancer patients. Am J Med. 1986;81A:11–25. - PubMed
-
- Cho YS, Choi HY. Opportunistic fungal infection among cancer patients. A ten year autopsy study. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979;72:617–22. - PubMed
-
- Epstein J, Truelove E, Izutau K. Oral candidiasis: pathogenesis and host defence. Rev Infect Dis. 1984;6:96–106. - PubMed
-
- Odds FC. Candida and Candidosis. London: Bailliere Tindall; 1988. Factors that predispose the host to candidosis; pp. 93–104.
-
- Brummer E, Stevens D. Candidacidal mechanisms of peritoneal macrophages activated with lymphokines or gamma interferon. J Med Microbiol. 1989;28:173–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

