Catheter-based endomyocardial injection with real-time magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 11901036
- PMCID: PMC1317571
- DOI: 10.1161/01.cir.0000012425.71261.fc
Catheter-based endomyocardial injection with real-time magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
Background: We tested the feasibility of targeted left ventricular (LV) mural injection using real-time MRI (rtMRI).
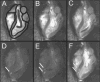
Methods and results: A 1.5T MRI scanner was customized with a fast reconstruction engine, transfemoral guiding catheter-receiver coil (GCC), MRI-compatible needle, and tableside consoles. Commercial real-time imaging software was customized to facilitate catheter navigation and visualization of injections at 4 completely refreshed frames per second. The aorta was traversed and the left ventricular cavity was entered under direct rtMRI guidance. Pigs underwent multiple injections with dilute gadolinium-DTPA. All myocardial segments were readily accessed. The active GCC and the passive Stiletto needle injector were readily visualized. More than 50 endomyocardial injections were performed with the aid of rtMRI; 81% were successful with this first-generation prototype.
Conclusion: Percutaneous endomyocardial drug delivery is feasible with the aid of rtMRI, which permits precise 3-dimensional localization of injection within the LV wall.
Figures

References
-
- Riederer SJ, Tasciyan T, Farzaneh F, et al. MR fluoroscopy: technical feasibility. Magn Reson Med. 1988;8:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Oppelt A. FISP—a new fast MRI sequence. Electromedica. 1986;54:15–18.
-
- Omary RA, Unal O, Koscielski DS, et al. Real-time MR imaging-guided passive catheter tracking with use of gadolinium-filled catheters. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2000;11:1079–1085. - PubMed
-
- Atalar E, Bottomley PA, Ocali O, et al. High resolution intravascular MRI and MRS by using a catheter receiver coil. Magn Reson Med. 1996;36:596–605. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

