Negative regulation of Lck by Cbl ubiquitin ligase
- PMID: 11904433
- PMCID: PMC122603
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.062055999
Negative regulation of Lck by Cbl ubiquitin ligase
Abstract
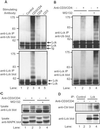
The Cbl-family ubiquitin ligases function as negative regulators of activated receptor tyrosine kinases by facilitating their ubiquitination and subsequent targeting to lysosomes. Cbl associates with the lymphoid-restricted nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Lck, but the functional relevance of this interaction remains unknown. Here, we demonstrate that T cell receptor and CD4 coligation on human T cells results in enhanced association between Cbl and Lck, together with Lck ubiquitination and degradation. A Cbl(-/-) T cell line showed a marked deficiency in Lck ubiquitination and increased levels of kinase-active Lck. Coexpression in 293T cells demonstrated that Lck kinase activity and Cbl ubiquitin ligase activity were essential for Lck ubiquitination and negative regulation of Lck-dependent serum response element-luciferase reporter activity. The Lck SH3 domain was pivotal for Cbl-Lck association and Cbl-mediated Lck degradation, with a smaller role for interactions mediated by the Cbl tyrosine kinase-binding domain. Finally, analysis of a ZAP-70-deficient T cell line revealed that Cbl inhibited Lck-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase activation, and an intact Cbl RING finger domain was required for this functional effect. Our results demonstrate a direct, ubiquitination-dependent, negative regulatory role of Cbl for Lck in T cells, independent of Cbl-mediated regulation of ZAP-70.
Figures
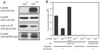




References
-
- Latour S, Veillette A. Curr Opin Immunol. 2001;13:299–306. - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Weiss A, Kumar G, Wang S, Nel A. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:17349–17357. - PubMed
-
- Molina T J, Kishihara K, Siderovski D P, van Ewijk W, Narendran A, Timms E, Wakeham A, Paige C J, Hartmann K U, Veillette A, et al. Nature (London) 1992;357:161–164. - PubMed
-
- Groves T, Smiley P, Cooke M P, Forbush K, Perlmutter R M, Guidos C J. Immunity. 1996;5:417–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

