Profound defects in pancreatic beta-cell function in mice with combined heterozygous mutations in Pdx-1, Hnf-1alpha, and Hnf-3beta
- PMID: 11904435
- PMCID: PMC122607
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.062605899
Profound defects in pancreatic beta-cell function in mice with combined heterozygous mutations in Pdx-1, Hnf-1alpha, and Hnf-3beta
Abstract
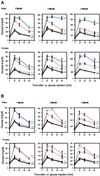
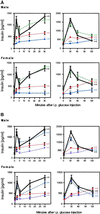
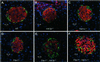
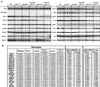
Defects in pancreatic beta-cell function contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes, a polygenic disease that is characterized by insulin resistance and compromised insulin secretion. Hepatocyte nuclear factors (HNFs) -1alpha, -3beta, -4alpha, and Pdx-1 contribute in the complex transcriptional circuits within the pancreas that are involved in beta-cell development and function. In mice, a heterozygous mutation in Pdx-1 alone, but not Hnf-1alpha(+/-), Hnf-3beta(+/-), or Hnf-4alpha(+/-), causes impaired glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in mice. To investigate the possible functional relationships between these transcription factors on beta-cell activity in vivo, we generated mice with the following combined heterozygous mutations: Pdx-1(+/-)/Hnf-1alpha(+/-), Pdx-1(+/-)/Hnf-3beta(+/-), Pdx-1(+/-)/Hnf-4alpha(+/-), Hnf-1alpha(+/-)/Hnf-4alpha(+/-), and Hnf-3beta(+/-)/Hnf-4alpha(+/-). The greatest loss in function was in combined heterozygous null alleles of Pdx-1 and Hnf-1alpha (Pdx-1(+/-)/Hnf-1alpha(+/-)), or Pdx-1 and Hnf-3beta (Pdx-1(+/-)/Hnf-3beta(+/-)). Both double mutants develop progressively impaired glucose tolerance and acquire a compromised first- and second-phase insulin secretion profile in response to glucose compared with Pdx-1(+/-) mice alone. The loss in beta-cell function in Pdx-1(+/-)/Hnf-3beta(+/-) mice was associated with decreased expression of Nkx-6.1, glucokinase (Gck), aldolase B (aldo-B), and insulin, whereas Nkx2.2, Nkx-6.1, Glut-2, Gck, aldo-B, the liver isoform of pyruvate kinase, and insulin expression was reduced in Pdx-1(+/-)/Hnf-1alpha(+/-) mice. The islet cell architecture was also abnormal in Pdx-1(+/-)/Hnf-3beta(+/-) and Pdx-1(+/-)/Hnf-1alpha(+/-) mice, with glucagon-expressing cells scattered throughout the islet, a defect that may be connected to decreased E-cadherin expression. Our data suggest that functional interactions between key islet regulatory factors play an important role in maintaining islet architecture and beta-cell function. These studies also established polygenic mouse models for investigating the mechanisms contributing to beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Edlund H. Diabetes. 2001;50, Suppl. 1:S5–S9. - PubMed
-
- Shih, D. Q. & Stoffel, M. (2002) Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2, in press. - PubMed
-
- St-Onge L, Wehr R, Gruss P. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999;9:295–300. - PubMed
-
- Sander M, Sussel L, Conners J, Scheel D, Kalamaras J, Dela Cruz F, Schwitzgebel V, Hayes-Jordan A, German M. Development (Cambridge, UK) 2000;127:5533–5540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

