Anti-secretory properties of non-peptide somatostatin receptor agonists in isolated rat colon: luminal activity and possible interaction with P-glycoprotein
- PMID: 11906957
- PMCID: PMC1573276
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704614
Anti-secretory properties of non-peptide somatostatin receptor agonists in isolated rat colon: luminal activity and possible interaction with P-glycoprotein
Abstract
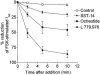
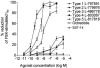
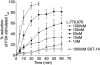
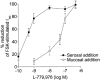
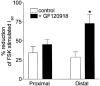
1. The diverse physiological actions of somatostatin are mediated by a family of G-protein coupled receptors (SSTRs). Several peptide analogues of somatostatin such as octreotide have been developed for therapeutic use, including treatment of gastrointestinal disorders such as secretory diarrhoea. However, their development as anti-diarrhoeal agents has been limited by poor oral bioavailability, necessitating parenteral administration. This in vitro study investigated the anti-secretory potential of a group of novel, non-peptide, somatostatin-receptor agonists that selectively activate specific SSTR subtypes to assess their potential for oral administration. 2. The ability of the agonists to inhibit forskolin-stimulated chloride secretion was measured using a sensitive bioassay system in isolated rat colonic mucosa. 3. The SSTR-2 selective agonist, L-779,976 was 10-times more potent than octreotide as an inhibitor of secretion when added to the basolateral surface of rat colon. Non-peptide agonists selective for SSTR1 (L-797,591), SSTR3 (L-796,778), SSTR4 (L-803,087) or SSTR5 (L-817,818) showed little or no anti-secretory activity in this preparation. 4. L-779,976 was able to inhibit secretion when applied to the luminal surface at sub-micromolar concentrations suggesting that it can cross the colonic epithelium. The anti-secretory potency of luminal L-779,976 was increased 3 fold in the presence of GF120918, a known inhibitor of P-glycoprotein. 5. Non-peptide somatostatin receptor agonists may provide a basis for the development of new, orally available anti-diarrhoeal therapies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Somatostatin receptor subtype 2 mediates somatostatin inhibition of ion secretion in rat distal colon.Gastroenterology. 1996 Aug;111(2):325-33. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v111.pm8690197. Gastroenterology. 1996. PMID: 8690197
-
Increased oral bioavailability of topotecan in combination with the breast cancer resistance protein and P-glycoprotein inhibitor GF120918.J Clin Oncol. 2002 Jul 1;20(13):2943-50. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.12.116. J Clin Oncol. 2002. PMID: 12089223 Clinical Trial.
-
Somatostatin decreases voltage-gated Ca2+ currents in GH3 cells through activation of somatostatin receptor 2.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Jun;292(6):E1863-70. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00047.2007. Epub 2007 Feb 27. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 17327372
-
Somatostatin and its receptor family.Front Neuroendocrinol. 1999 Jul;20(3):157-98. doi: 10.1006/frne.1999.0183. Front Neuroendocrinol. 1999. PMID: 10433861 Review.
-
Somatostatin receptors in pituitary and development of somatostatin receptor subtype-selective analogs.Endocrine. 2003 Apr;20(3):265-9. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:20:3:265. Endocrine. 2003. PMID: 12721506 Review.
Cited by
-
5-HT(1A), SST(1), and SST(2) receptors mediate inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in the submucous plexus of the guinea pig ileum.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010 Mar;298(3):G384-94. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00438.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 10. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20007849 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic advances in functional gastrointestinal disease: irritable bowel syndrome.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2009 May 1;2(3):169-181. doi: 10.1177/1756283X08103656. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19936327 Free PMC article.
-
Cholera and Pancreatic Cholera: Is VIP the Common Pathophysiologic Factor?Trop Med Infect Dis. 2020 Jul 2;5(3):111. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed5030111. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32630790 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin and Its Receptor System in Colorectal Cancer.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 22;9(11):1743. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111743. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene expression profile of duodenal epithelial cells in response to chronic metabolic acidosis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Jan;321(1-2):173-88. doi: 10.1007/s11010-008-9931-1. Epub 2008 Nov 4. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 18979233
References
-
- CREUTZFELDT W., LEMBKE B., FOLSCH U.R., SCHLESER S., KOOP I. Effect of somatostatin analogue (SMS 201-995, Sandostatin) on pancreatic secretion in humans. Am. J. Med. 1987;82:49–54. - PubMed
-
- CSABA Z., DOURNAUD P. Cellular biology of somatostatin receptors. Neuropeptides. 2001;35:1–23. - PubMed
-
- DE BRUIN M., MIYAKE K., LITMAN T., ROBEY R., BATES S.E. Reversal of resistance by GF120918 in cells expressing the ABC half-transporter, MXR. Cancer Lett. 1999;146:117–126. - PubMed
-
- FARTHING M.J. Chronic diarrhoea: Current concepts on mechanisms and management. Eur. J. Gastro. Hepatol. 1996;8:157–167. - PubMed
-
- FREIDINGER R.M. Non-peptidic ligands for peptide and protein receptors. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1999;3:395–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

