Subcellular localization and topology of the p7 polypeptide of hepatitis C virus
- PMID: 11907211
- PMCID: PMC136108
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.8.3720-3730.2002
Subcellular localization and topology of the p7 polypeptide of hepatitis C virus
Abstract
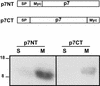
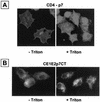
Although biological and biochemical data have been accumulated on most hepatitis C virus proteins, the structure and function of the 63-amino-acid p7 polypeptide of this virus have never been investigated. In this work, sequence analyses predicted that p7 contains two transmembrane passages connected by a short hydrophilic segment. The C-terminal transmembrane domain of p7 was predicted to function as a signal sequence, which was confirmed experimentally by analyzing the translocation of a reporter glycoprotein fused at its C terminus. The p7 polypeptide was tagged either with the ectodomain of CD4 or with a Myc epitope to study its membrane integration, its subcellular localization, and its topology. Alkaline extraction studies confirmed that p7 is an integral membrane polypeptide. The CD4-p7 chimera was detected by immunofluorescence on the surface of nonpermeabilized cells, indicating that it is exported to the plasma membrane. However, pulse-chase analyses showed that only approximately 20% of endoglycosidase H-resistant CD4-p7 was detected after long chase times, suggesting that a large proportion of p7 stays in an early compartment of the secretory pathway. Finally, by inserting a Myc epitope in several positions of p7 and analyzing the accessibility of this epitope on the plasma membrane of HepG2 cells, we showed that p7 has a double membrane-spanning topology, with both its N and C termini oriented toward the extracellular environment. Altogether, these data indicate that p7 is a polytopic membrane protein that could have a functional role in several compartments of the secretory pathway.
Figures






References
-
- Becher, P., M. Konig, D. J. Paton, and H. J. Thiel. 1995. Further characterization of border disease virus isolates: evidence for the presence of more than three species within the genus pestivirus. Virology 209:200-206. - PubMed
-
- Blanchet, C., C. Combet, C. Geourjon, and G. Deléage. 2000. MPSA: integrated system for multiple protein sequence analysis with client/server capabilities. Bioinformatics 16:286-287. - PubMed
-
- Claros, M. G., and G. von Heijne. 1994. TopPred II: an improved software for membrane protein structure predictions. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 269:26898-26903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

