Stretch-regulated exocytosis/endocytosis in bladder umbrella cells
- PMID: 11907265
- PMCID: PMC99602
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.01-09-0435
Stretch-regulated exocytosis/endocytosis in bladder umbrella cells
Abstract
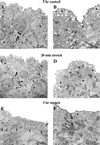
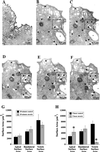
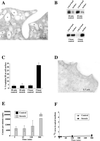
The epithelium of the urinary bladder must maintain a highly impermeable barrier despite large variations in urine volume during bladder filling and voiding. To study how the epithelium accommodates these volume changes, we mounted bladder tissue in modified Ussing chambers and subjected the tissue to mechanical stretch. Stretching the tissue for 5 h resulted in a 50% increase in lumenal surface area (from approximately 2900 to 4300 microm(2)), exocytosis of a population of discoidal vesicles located in the apical cytoplasm of the superficial umbrella cells, and release of secretory proteins. Surprisingly, stretch also induced endocytosis of apical membrane and 100% of biotin-labeled membrane was internalized within 5 min after stretch. The endocytosed membrane was delivered to lysosomes and degraded by a leupeptin-sensitive pathway. Last, we show that the exocytic events were mediated, in part, by a cyclic adenosine monophosphate, protein kinase A-dependent process. Our results indicate that stretch modulates mucosal surface area by coordinating both exocytosis and endocytosis at the apical membrane of umbrella cells and provide insight into the mechanism of how mechanical forces regulate membrane traffic in non-excitable cells.
Figures

References
-
- Amano O, Kataoka S, Yamamoto T. Turnover of asymmetric unit membranes in the transitional epithelial superficial cells of the rat urinary bladder. Anat Rec. 1991;229:9–15. - PubMed
-
- Apodaca G. Modulation of membrane traffic by mechanical stimuli. Am J Physiol. 2002;282:F179–F190. - PubMed
-
- Baddeley A, Gunderson H, Cruz-Orive L. Estimation of surface area from vertical sections. J Microsc. 1986;142:259–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

