FBI-1 can stimulate HIV-1 Tat activity and is targeted to a novel subnuclear domain that includes the Tat-P-TEFb-containing nuclear speckles
- PMID: 11907272
- PMCID: PMC99609
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.01-08-0383
FBI-1 can stimulate HIV-1 Tat activity and is targeted to a novel subnuclear domain that includes the Tat-P-TEFb-containing nuclear speckles
Abstract
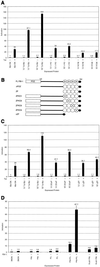
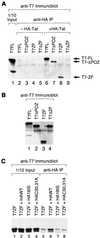
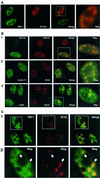
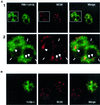
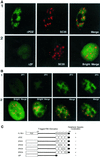
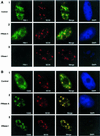
FBI-1 is a cellular POZ-domain-containing protein that binds to the HIV-1 LTR and associates with the HIV-1 transactivator protein Tat. Here we show that elevated levels of FBI-1 specifically stimulate Tat activity and that this effect is dependent on the same domain of FBI-1 that mediates Tat-FBI-1 association in vivo. FBI-1 also partially colocalizes with Tat and Tat's cellular cofactor, P-TEFb (Cdk9 and cyclin T1), at the splicing-factor-rich nuclear speckle domain. Further, a less-soluble population of FBI-1 distributes in a novel peripheral-speckle pattern of localization as well as in other nuclear regions. This distribution pattern is dependent on the FBI-1 DNA binding domain, on the presence of cellular DNA, and on active transcription. Taken together, these results suggest that FBI-1 is a cellular factor that preferentially associates with active chromatin and that can specifically stimulate Tat-activated HIV-1 transcription.
Figures

References
-
- Albagli O, Dhordain P, Deweindt C, Lecocq G, Leprince D. The BTB/POZ domain: a new protein-protein interaction motif common to DNA- and actin-binding proteins. Cell Growth Differ. 1995;6:1193–1198. - PubMed
-
- Bardwell VJ, Treisman R. The POZ domain: a conserved protein-protein interaction motif. Genes Dev. 1994;8:1664–1677. - PubMed
-
- Baron BW, Desai M, Baber LJ, Paras L, Zhang Q, Sadhu A, Duguay S, Nucifora G, McKeithan TW, Zeleznik-Le N. BCL6 can repress transcription from the human immunodeficiency virus type I promoter/enhancer region. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1997;19:14–21. - PubMed
-
- Bustin M, Trieschmann L, Postnikov YV. The HMG-14/-17 chromosomal protein family: architectural elements that enhance transcription from chromatin templates. Semin Cell Biol. 1995;6:247–255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

