In vivo analysis of the role of atTic20 in protein import into chloroplasts
- PMID: 11910011
- PMCID: PMC150586
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.010336
In vivo analysis of the role of atTic20 in protein import into chloroplasts
Abstract
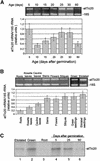
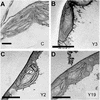
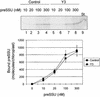
The import of nucleus-encoded preproteins into plastids requires the coordinated activities of membrane protein complexes that facilitate the translocation of polypeptides across the envelope double membrane. Tic20 was identified previously as a component of the import machinery of the inner envelope membrane by covalent cross-linking studies with trapped preprotein import intermediates. To investigate the role of Tic20 in preprotein import, we altered the expression of the Arabidopsis Tic20 ortholog (atTic20) by antisense expression. Several antisense lines exhibited pronounced chloroplast defects exemplified by pale leaves, reduced accumulation of plastid proteins, and significant growth defects. The severity of the phenotypes correlated directly with the reduction in levels of atTic20 expression. In vitro import studies with plastids isolated from control and antisense plants indicated that the antisense plastids are defective specifically in protein translocation across the inner envelope membrane. These data suggest that Tic20 functions as a component of the protein-conducting channel at the inner envelope membrane.
Figures




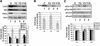

Similar articles
-
In vivo studies on the roles of two closely related Arabidopsis Tic20 proteins, AtTic20-I and AtTic20-IV.Plant Cell Physiol. 2011 Mar;52(3):469-78. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcr010. Epub 2011 Jan 25. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21266460
-
Molecular and genetic analyses of Tic20 homologues in Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplasts.Plant J. 2011 Jun;66(5):877-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04551.x. Epub 2011 Apr 4. Plant J. 2011. PMID: 21395885
-
Tic21 is an essential translocon component for protein translocation across the chloroplast inner envelope membrane.Plant Cell. 2006 Sep;18(9):2247-57. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.044305. Epub 2006 Aug 4. Plant Cell. 2006. PMID: 16891400 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of protein import across the chloroplast envelope.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):485-91. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10961945 Review.
-
The TOC GTPase Receptors: Regulators of the Fidelity, Specificity and Substrate Profiles of the General Protein Import Machinery of Chloroplasts.Protein J. 2019 Jun;38(3):343-350. doi: 10.1007/s10930-019-09846-3. Protein J. 2019. PMID: 31201619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Plant Transcriptome Profiling of Arabidopsis thaliana Col-0 and Camelina sativa var. Celine Infested with Myzus persicae Aphids Acquiring Circulative and Noncirculative Viruses Reveals Virus- and Plant-Specific Alterations Relevant to Aphid Feeding Behavior and Transmission.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0013622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00136-22. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35856906 Free PMC article.
-
The FAST technique: a simplified Agrobacterium-based transformation method for transient gene expression analysis in seedlings of Arabidopsis and other plant species.Plant Methods. 2009 May 20;5:6. doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-5-6. Plant Methods. 2009. PMID: 19457242 Free PMC article.
-
A Protochlorophyllide (Pchlide) a Oxygenase for Plant Viability.Front Plant Sci. 2019 May 15;10:593. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00593. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31156665 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Protein Import into Chloroplasts Isolated from Stressed Plants.J Vis Exp. 2016 Nov 1;(117):54717. doi: 10.3791/54717. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 27842368 Free PMC article.
-
The localization of Tic20 proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana is not restricted to the inner envelope membrane of chloroplasts.Plant Mol Biol. 2011 Nov;77(4-5):381-90. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9818-5. Epub 2011 Aug 28. Plant Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21874592
References
-
- Aronsson, H., Sohrt, K., and Soll, J. (2000). NADPH:protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase uses the general import route into chloroplasts. Biol. Chem. 381, 1263–1267. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, J., Chen, K., Hiltbrunner, A., Wehrli, E., Eugster, M., Schnell, D., and Kessler, F. (2000. a). The major protein import receptor of plastids is essential for chloroplast biogenesis. Nature 403, 203–207. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, M.F., Hofmann, S., Neupert, W., and Brunner, M. (2000. b). Protein translocation into mitochondria: The role of TIM complexes. Trends Cell Biol. 10, 25–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

