Zein protein interactions, rather than the asymmetric distribution of zein mRNAs on endoplasmic reticulum membranes, influence protein body formation in maize endosperm
- PMID: 11910012
- PMCID: PMC150587
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.010431
Zein protein interactions, rather than the asymmetric distribution of zein mRNAs on endoplasmic reticulum membranes, influence protein body formation in maize endosperm
Abstract
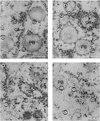
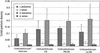
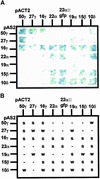
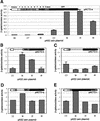
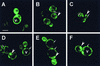
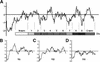
Prolamin-containing protein bodies in maize endosperm are composed of four different polypeptides, the alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and delta-zeins. The spatial organization of zeins within the protein body, as well as interactions between them, suggests that the localized synthesis of gamma-zeins could initiate and target protein body formation at specific regions of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. To investigate this possibility, we analyzed the distribution of mRNAs encoding the 22-kD alpha-zein and the 27-kD gamma-zein proteins on cisternal and protein body rough endoplasmic reticulum membranes. In situ hybridization revealed similar frequencies of the mRNAs in both regions of the endoplasmic reticulum, indicating that the transcripts are distributed more or less randomly. This finding implies that zein protein interactions determine protein body assembly. To address this question, we expressed cDNAs encoding alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and delta-zeins in the yeast two-hybrid system. We found strong interactions among the 50-, 27-, and 16-kD gamma-zeins and the 15-kD beta-zein, consistent with their colocalization in developing protein bodies. Interactions between the 19- and 22-kD alpha-zeins were relatively weak, although each of them interacted strongly with the 10-kD delta-zein. Strong interactions were detected between the alpha- and delta-zeins and the 16-kD gamma-zein and the 15-kD beta-zein; however, the 50- and 27-kD gamma-zeins did not interact with the alpha- and delta-zein proteins. We identified domains within the 22-kD alpha-zein that bound preferentially the alpha- and delta-zeins and the beta- and gamma-zeins. Affinities between zeins generally were consistent with results from immunolocalization experiments, suggesting an important role for the 16-kD gamma-zein and the 15-kD beta-zein in the binding and assembly of alpha-zeins within the protein body.
Figures



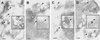
Similar articles
-
Genomics analysis of genes expressed in maize endosperm identifies novel seed proteins and clarifies patterns of zein gene expression.Plant Cell. 2001 Oct;13(10):2297-317. doi: 10.1105/tpc.010240. Plant Cell. 2001. PMID: 11595803 Free PMC article.
-
The maize floury1 gene encodes a novel endoplasmic reticulum protein involved in zein protein body formation.Plant Cell. 2007 Aug;19(8):2569-82. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.053538. Epub 2007 Aug 10. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 17693529 Free PMC article.
-
The maize gamma-zein sequesters alpha-zein and stabilizes its accumulation in protein bodies of transgenic tobacco endosperm.Plant Cell. 1996 Dec;8(12):2335-45. doi: 10.1105/tpc.8.12.2335. Plant Cell. 1996. PMID: 8989886 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of zein biosynthesis in maize endosperm.Theor Appl Genet. 2020 May;133(5):1443-1453. doi: 10.1007/s00122-019-03520-z. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Theor Appl Genet. 2020. PMID: 31897513 Review.
-
Proteome balancing of the maize seed for higher nutritional value.Front Plant Sci. 2014 May 30;5:240. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00240. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24910639 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nonredundant function of zeins and their correct stoichiometric ratio drive protein body formation in maize endosperm.Plant Physiol. 2013 Jul;162(3):1359-69. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.218941. Epub 2013 May 15. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23677936 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptomics reveals the difference in early endosperm development between maize with different amylose contents.PeerJ. 2019 Aug 28;7:e7528. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7528. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31523504 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Transcriptome-Based Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis Reveals Key Modules and Hub Genes Associated With the Structure and Nutrient Formation of Endosperm for Wax Corn.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 9;13:915400. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.915400. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35755662 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of prolamins to the protein storage vacuole in maize aleurone cells.Plant Cell. 2011 Feb;23(2):769-84. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.082156. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 21343414 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of Maize floury4 as a Novel Semidominant Opaque Mutant That Disrupts Protein Body Assembly.Plant Physiol. 2014 Jun;165(2):582-594. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.238030. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24706551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe, S., You, W., and Davies, E. (1991). Protein bodies in corn endosperm are enclosed by and enmeshed in F-actin. Protoplasma 165, 139–149.
-
- Argos, P., Pedersen, K., Marks, M.D., and Larkins, B.A. (1982). A structural model for maize zein proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 9984–9990. - PubMed
-
- Bai, C., and Elledge, S.J. (1996). Gene identification using the yeast two-hybrid system. Methods Enzymol. 273, 331–347. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Peled, M., Bassham, D.C., and Raikhel, N.V. (1996). Transport of proteins in eukaryotic cells: More questions ahead. Plant Mol. Biol. 32, 223–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

