Prediction of gene function in methylthioadenosine recycling from regulatory signals
- PMID: 11914366
- PMCID: PMC134950
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.8.2314-2318.2002
Prediction of gene function in methylthioadenosine recycling from regulatory signals
Abstract
The S-box transcription termination control system, first identified in Bacillus subtilis, is used for regulation of gene expression in response to methionine availability. The presence of the S-box motif provided the first indication that the ykrTS and ykrWXYZ genes could play a role in recycling of 5'-methylthioadenosine, a by-product of polyamine biosynthesis that can be converted to methionine. In this study we demonstrate a role for the ykrTS and ykrWXYZ gene products in this pathway.
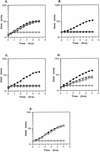
Figures

References
-
- Cornell, K. A., and M. K. Riscoe. 1998. Cloning and expression of Escherichia coli 5′-methylthioadenosine/S-adenosylhomocysteine nucleosidase: identification of the pfs gene product. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1396:8-14. - PubMed
-
- Duerre, J. A. 1962. A hydrolytic nucleosidase acting on S-adenosylhomocysteine and on 5′-methylthioadenosine. J. Biol. Chem. 237:3737-3741.
-
- Ferro, A. J., A. Barrett, and S. K. Shapiro. 1978. 5-methylthioribose kinase. A new enzyme involved in the formation of methionine from 5-methylthioribose. J. Biol. Chem. 253:6021-6025. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

