Degradation of 17beta-estradiol by a gram-negative bacterium isolated from activated sludge in a sewage treatment plant in Tokyo, Japan
- PMID: 11916733
- PMCID: PMC123865
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.68.4.2057-2060.2002
Degradation of 17beta-estradiol by a gram-negative bacterium isolated from activated sludge in a sewage treatment plant in Tokyo, Japan
Abstract
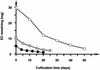
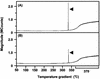
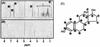
A 17beta-estradiol (E2)-degrading bacterium was isolated from activated sludge in a sewage treatment plant in Tokyo, Japan. The isolate was suggested to be a new Novosphingobium species. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance analyses of the metabolites of E2 degradation suggested that no toxic products accumulated in the culture medium.
Figures
References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic logical alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Baronti, C., R. Curini, G. D'Ascenzo, A. Di Corcia, A. Gentili, and R. Sampeli. 2000. Monitoring natural and synthetic estrogens at activated sludge sewage treatment plants and in a receiving river water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 34:5059-5066.
-
- Desbrow, C., E. J. Routledge, G. C. Brighty, J. P. Sumpter, and M. Waldock. 1998. Identification of estrogenic chemicals in STW effluent. 1. Chemical fractionation and in vitro biological screening. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32:1549-1558.
-
- Folmar, L. C., N. D. Denslow, V. Rao, M. Chow, D. A. Crain, J. Enbrom, J. Marcino, and L. J. Guillette, Jr. 1996. Vitellogenin induction and reduced serum testosterone concentrations in feral male carp (Cyprinus carpio) captured near major metropolitan sewage treatment plant. Environ. Health Perspect. 104:1096-1101. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

