Naive T cells proliferate strongly in neonatal mice in response to self-peptide/self-MHC complexes
- PMID: 11917110
- PMCID: PMC123683
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.062621699
Naive T cells proliferate strongly in neonatal mice in response to self-peptide/self-MHC complexes
Abstract
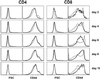
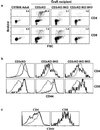
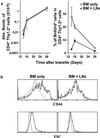
Adult naive T cells, which are at rest in normal conditions, proliferate strongly when transferred to lymphopenic hosts. In neonates, the first mature thymocytes to migrate to the periphery reach a compartment devoid of preexisting T cells. We have extensively analyzed the proliferation rate and phenotype of peripheral T cells from normal C57BL/6 and T cell antigen receptor transgenic mice as a function of age. We show that, like adult naive T cells transferred to lymphopenic mice, neonatal naive T cells proliferate strongly. By using bone-marrow transfer and thymic-graft models, we demonstrate that the proliferation of the first thymic emigrants reaching the periphery requires T cell antigen receptor-self-peptide/self-MHC interactions and is regulated by the size of the peripheral T cell pool.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

