Hepatic arterioportal shunts: dynamic CT and MR features
- PMID: 11919473
- PMCID: PMC2713981
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2002.3.1.1
Hepatic arterioportal shunts: dynamic CT and MR features
Abstract
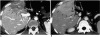
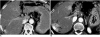
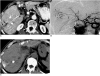
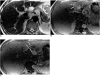
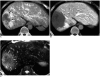
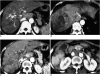
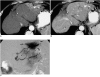
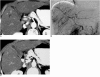
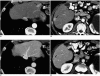
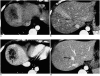
With the increased temporal resolution available in dynamic computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), hepatic arterioportal shunts are now more frequently encountered than in the past. The condition occurs in various hepatic diseases in which portal or hepatic venous flow is compromised. The underlying mechanism and the degree of shunt affect its appearance at dynamic imaging. The dynamic CT and MRI findings have been summarized as early enhancement of peripheral portal veins, and wedge-shaped transient parenchymal enhancement during the hepatic arterial phase. Recognition of arterioportal shunt can suggest the presence of a previously unsuspected disorder and avoids false-positive diagnosis or overestimation of a hepatic disease. Familiarity with the pathophysiology of arterioportal shunt also allows investigation of the hepatic hemodynamic changes occurring in various hepatic diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Choi BI, Chung JW, Itai Y, Matsui O, Han JK, Han MC. Hepatic abnormalities related to blood flow: evaluation with dual-phase helical CT. Abdom Imaging. 1999;24:340–356. - PubMed
-
- Ternberg JL, Butcher HR., Jr Blood flow relation between hepatic artery and portal vein. Science. 1965;150:1030–1031. - PubMed
-
- Itai Y, Matsui O. Blood flow and liver imaging. Radiology. 1997;202:306–314. - PubMed
-
- McCuskey RS. A dynamic and static study of hepatic arterioles and hepatic sphincters. Am J Anat. 1966;119:455–477. - PubMed
-
- Bookstein JJ, Cho KJ, Davis GB, Dail D. Arterioportal communications: observations and hypotheses concerning transsinusoidal and transvasal types. Radiology. 1982;142:581–590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

