PARK3 influences age at onset in Parkinson disease: a genome scan in the GenePD study
- PMID: 11920285
- PMCID: PMC447587
- DOI: 10.1086/339814
PARK3 influences age at onset in Parkinson disease: a genome scan in the GenePD study
Abstract
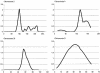
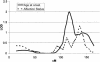
Parkinson disease (PD) is a late-onset neurodegenerative disorder. The mean age at onset is 61 years, but the disease can range from juvenile cases to cases in the 8th or 9th decade of life. The parkin gene on chromosome 6q and loci on chromosome 1p35-36 and 1p36 are responsible for some cases of autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism, but they do not appear to influence susceptibility or variability of age at onset for idiopathic PD. We have performed a genomewide linkage analysis using variance-component methodology to identify genes influencing age at onset of PD in a population of affected relatives (mainly affected sibling pairs) participating in the GenePD study. Four chromosomal loci showed suggestive evidence of linkage: chromosome 2p (maximum multipoint LOD [MaxLOD] = 2.08), chromosome 9q (MaxLOD = 2.00), chromosome 20 (MaxLOD = 1.82), and chromosome 21 (MaxLOD = 2.21). The 2p and 9q locations that we report here have previously been reported as loci influencing PD affection status. Association between PD age at onset and allele 174 of marker D2S1394, located on 2p13, was observed in the GenePD sample (P=.02). This 174 allele is common to the PD haplotype observed in two families that show linkage to PARK3 and have autosomal dominant PD, which suggests that this allele may be in linkage disequilibrium with a mutation influencing PD susceptibility or age at onset of PD.
Figures
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- ASPEX Linkage Analysis Package, The, ftp://lahmed.stanford.edu/pub/aspex/index.html
-
- FBAT Web Page, http://www.biostat.harvard.edu/~fbat/default.html
References
-
- Cardno AG, Holmans PA, Rees MI, Jones LA, McCarthy GM, Hamshere ML, Williams NM, Norton N, Williams HJ, Fenton I, Murphy KC, Sanders RD, Gray MY, O'Donovan MC, McGuffin P, Owen MJ (2001) A genomewide linkage study of age at onset in schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet 105:439–445 - PubMed
-
- DeStefano AL, Golbe LI, Mark MH, Lazzarini AM, Maher NE, Saint-Hilaire M, Feldman RG, et al (2001) Genome-wide scan for Parkinson's disease: the GenePD study. Neurology 57:1124–1126 - PubMed
-
- Farrer M, Gwinn-Hardy K, Muenter M, DeVrieze FW, Crook R, Perez-Tur J, Lincoln S, Maraganore D, Adler C, Newman S, MacElwee K, McCarthy P, Miller C, Waters C, Hardy J (1999) A chromosome 4p haplotype segregating with Parkinson's disease and postural tremor. Hum Mol Genet 8:81–85 - PubMed
-
- Gasser T, Muller-Myhsok B, Wszolek ZK, Oehlmann R, Calne DB, Bonifati V, Bereznai B, Fabrizio E, Vieregge P, Horstmann RD (1998) A susceptibility locus for Parkinson's disease maps to chromosome 2p13. Nat Genet 18:262–265 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

