Mapping of gene loci for nephronophthisis type 4 and Senior-Løken syndrome, to chromosome 1p36
- PMID: 11920287
- PMCID: PMC447598
- DOI: 10.1086/340317
Mapping of gene loci for nephronophthisis type 4 and Senior-Løken syndrome, to chromosome 1p36
Abstract
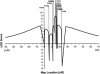
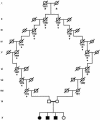
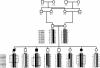
For nephronophthisis (NPHP), the primary genetic cause of chronic renal failure in young adults, three loci have been mapped. To identify a new locus for NPHP, we here report on total-genome linkage analysis in seven families with NPHP, in whom we had excluded linkage to all three known NPHP loci. LOD scores >1 were obtained at nine loci, which were then fine mapped at 1-cM intervals. Extensive total-genome haplotype analysis revealed homozygosity in one family, in the region of the PCLN1 gene. Subsequent mutational analysis in this gene revealed PCLN1 mutations, thereby allowing exclusion of this family as a phenocopy. Multipoint linkage analysis for the remaining six families with NPHP together yielded a maximum LOD score (Z(max)) of 8.9 (at D1S253). We thus identified a new locus, NPHP4, for nephronophthisis. Markers D1S2660 and D1S2642 are flanking NPHP4 at a 2.9-cM critical interval. In one family with NPHP4, extensive genealogical studies were conducted, revealing consanguinity during the 17th century. On the basis of haplotype sharing by descent, we obtained a multipoint Z(max) of 5.8 for D1S253 in this kindred alone. In addition, we were able to localize to the NPHP4 locus a new locus for Senior-Løken syndrome, an NPHP variant associated with retinitis pigmentosa.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Généthon, http://www.genethon.fr/ (for map positions)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for NPHP1 [MIM 256100], NPHP2 [MIM 602088], NPHP3 [MIM 604387], SLS [MIM 266900], and FHHN [MIM 603959])
-
- Project Ensembl, http://www.ensembl.org
References
-
- Antignac C, Arduy C, Beckmann JS, Benessy F, Gros F, Medhioub M, Hildebrandt F, Dufier JL, Kleinknecht C, Broyer M (1993) A gene for familial juvenile nephronophthisis (recessive medullary cystic disease) maps to chromosome 2p. Nat Genet 3:342–345 - PubMed
-
- Barnes KC, Mathias RA, Nickel R, Freidhoff LR, Stockton ML, Xue X, Naidu RP, Levett PN, Casolaro V, Beaty TH (2001) Testing for gene-gene interaction controlling total IgE in families from Barbados: evidence of sensitivity regarding linkage heterogeneity among families. Genomics 71:246–251 - PubMed
-
- Caridi G, Murer L, Bellantuono R, Sorino P, Caringella DA, Gusmano R, Ghiggeri GM (1998) Renal-retinal syndromes: association of retinal anomalies and recessive nephronophthisis in patients with homozygous deletion of the NPH1 locus. Am J Kidney Dis 32:1059–1062 - PubMed
-
- Conneally PM, Edwards JH, Kidd KK, Lalouel JM, Morton NE, Ott J, White R (1985) Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet 40:356–359 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

