Construction of cDNA representational difference analysis based on two cDNA libraries and identification of garlic inducible expression genes in human gastric cancer cells
- PMID: 11925593
- PMCID: PMC4658352
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i2.208
Construction of cDNA representational difference analysis based on two cDNA libraries and identification of garlic inducible expression genes in human gastric cancer cells
Abstract
Aim: To elucidate molecular mechanism of chemopreventive efficacies of garlic against human gastric cancer (HGC).
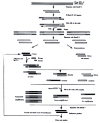
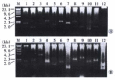
Methods: HGC cell line BGC823 was treated with Allitridi (a kind of garlic extract) and Allitridi-treated and parental BGC823 cDNA libraries were constructed respectively by using lambdaZAP II vector. cDNA Representational Difference Analysis (cDNA RDA) was performed using Bam H I cutting-site and abundant cDNA messages provided by the libraries. Northern blot analysis was applied to identify the obtained difference products.
Results: Two specific cDNA fragments were obtained and characterized to be derived from homo sapiens folate receptor alpha (FRalpha) gene and calcyclin gene respectively. Northern blot results showed a 4-fold increase in FRalpha gene expression level and 9-fold increase in calcyclin mRNA level in BGC823 cells after Allitridi treatment for 72h.
Conclusion: The method of cDNA RDA based on cDNA libraries combines the high specificity of cDNA RDA with abundant cDNA messages in cDNA library; this expands the application of cDNA library and increases the specificity of cDNA RDA. Up-regulation of FRalpha gene and calcyclin gene expressions induced by Allitridi provide valuable molecular evidence for the efficacy garlic in treating HGC as well as other diseases.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

