CLAC: a novel Alzheimer amyloid plaque component derived from a transmembrane precursor, CLAC-P/collagen type XXV
- PMID: 11927537
- PMCID: PMC125364
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/21.7.1524
CLAC: a novel Alzheimer amyloid plaque component derived from a transmembrane precursor, CLAC-P/collagen type XXV
Abstract
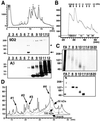
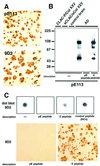
We raised monoclonal antibodies against senile plaque (SP) amyloid and obtained a clone 9D2, which labeled amyloid fibrils in SPs and reacted with approximately 50/100 kDa polypeptides in Alzheimer's disease (AD) brains. We purified the 9D2 antigens and cloned a cDNA encoding its precursor, which was a novel type II transmembrane protein specifically expressed in neurons. This precursor harbored three collagen-like Gly-X-Y repeat motifs and was partially homologous to collagen type XIII. Thus, we named the 9D2 antigen as CLAC (collagen-like Alzheimer amyloid plaque component), and its precursor as CLAC-P/collagen type XXV. The extracellular domain of CLAC-P/collagen type XXV was secreted by furin convertase, and the N-terminus of CLAC deposited in AD brains was pyroglutamate modified. Both secreted and membrane-tethered forms of CLAC-P/collagen type XXV specifically bound to fibrillized Abeta, implicating these proteins in beta-amyloidogenesis and neuronal degeneration in AD.
Figures






References
-
- Brady M.A.W. and Finlan,M.F. (1990) Radioactive labels: autoradiography and choice of emulsions for in situ hybridization. In Polak,J.M. and McGee,J.O’D. (eds), In situ Hybridization, Principles and Practice. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, pp. 31–57.
-
- Bruckner P. and Prockop,D.J. (1981) Proteolytic enzymes as probes for the triple-helical conformation of procollagen. Anal. Biochem., 110, 360–368. - PubMed
-
- Dickson D.W. (1997) The pathogenesis of senile plaques. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 56, 321–339. - PubMed
-
- Duff K. et al. (1996) Increased amyloid-β42(43) in brains of mice expressing mutant presenilin 1. Nature, 383, 710–713. - PubMed
-
- Duguay S.J., Lai-Zhang,J. and Steiner,D.F. (1995) Mutational analysis of the insulin-like growth factor I prohormone processing site. J. Biol. Chem., 270, 17566–17574. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

