IdeS, a novel streptococcal cysteine proteinase with unique specificity for immunoglobulin G
- PMID: 11927545
- PMCID: PMC125946
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/21.7.1607
IdeS, a novel streptococcal cysteine proteinase with unique specificity for immunoglobulin G
Abstract
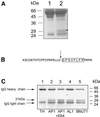
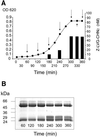
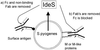
Recent work from several laboratories has demonstrated that proteolytic mechanisms significantly contribute to the molecular interplay between Streptococcus pyogenes, an important human pathogen, and its host. Here we describe the identification, purification and characterization of a novel extracellular cysteine proteinase produced by S.pyogenes. This enzyme, designated IdeS for Immunoglobulin G-degrading enzyme of S.pyogenes, is distinct from the well-characterized streptococcal cysteine proteinase, SpeB, and cleaves human IgG in the hinge region with a high degree of specificity. Thus, other human proteins, including immunoglobulins M, A, D and E, are not degraded by IdeS. The enzyme efficiently cleaves IgG antibodies bound to streptococcal surface structures, thereby inhibiting the killing of S.pyogenes by phagocytic cells. This and additional observations on the distribution and expression of the ideS gene indicate that IdeS represents a novel and significant bacterial virulence determinant, and a potential therapeutic target.
Figures




References
-
- Abrahamson M., Ritonja,A., Brown,M.A., Grubb,A., Machleidt,W. and Barrett,A.J. (1987) Identification of the probable inhibitory reactive sites of the cysteine proteinase inhibitors human cystatin C and chicken cystatin. J. Biol. Chem., 262, 9688–9694. - PubMed
-
- Åkesson P., Cooney, J., Kishimoto,F. and Björck,L. (1990) Protein H— a novel IgG binding bacterial protein. Mol. Immunol., 27, 523–531. - PubMed
-
- Altschul S.F., Gish,W., Miller,W., Myers,E.W. and Lipman,D.J. (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol., 215, 403–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

