Hypothalamic Y2 receptors regulate bone formation
- PMID: 11927618
- PMCID: PMC150931
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI14588
Hypothalamic Y2 receptors regulate bone formation
Abstract
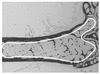
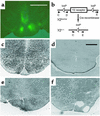
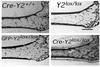
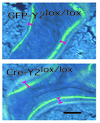
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is a downstream modulator of leptin action, possibly at the level of the arcuate nucleus where NPY neurons are known to express both leptin receptors and Y2 receptors. In addition to the well-described role of NPY and leptin in energy balance and obesity, intracerebroventricular administration of NPY or leptin also causes bone loss. Here we show that Y2 receptor-deficient mice have a twofold increase in trabecular bone volume as well as greater trabecular number and thickness compared with control mice. We also demonstrate that central Y2 receptors are crucial for this process, since selective deletion of hypothalamic Y2 receptors in mature conditional Y2 knockout mice results in an identical increase in trabecular bone volume within 5 weeks. This hypothalamus-specific Y2 receptor deletion stimulates osteoblast activity and increases the rate of bone mineralization and formation, with no effect on osteoblast or osteoclast surface measurements. The lack of any changes in plasma total calcium, leptinemia, or hypothalamo-pituitary-corticotropic, -thyrotropic, -somatotropic, or -gonadotropic output suggests that Y2 receptors do not modulate bone formation by humoral mechanisms, and that alteration of autonomic function through hypothalamic Y2 receptors may play a key role in a major central regulatory circuit of bone formation.
Figures
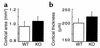
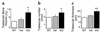


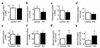
References
-
- Stephens TW, et al. The role of neuropeptide Y in the antiobesity action of the obesegene product. Nature. 1995;377:530–532. - PubMed
-
- Coleman, D.L. 1988. Classical diabetes models: past lessons and potential new therapies. In Frontiers in diabetes research. Lessons from animal diabetes II. E. Shafrir and A.E. Renold, editors. John Libbey & Co. London, United Kingdom. 253–256.
-
- Erickson JC, Hollopeter G, Palmiter RD. Attenuation of the obesity syndrome of ob/ob mice by the loss of neuropeptide Y. Science. 1996;274:1704–1707. - PubMed
-
- Ducy P, et al. Leptin inhibits bone formation through a hypothalamic relay: a central control of bone mass. Cell. 2000;100:197–207. - PubMed
-
- Sainsbury A, Cusin I, Doyle P, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Jeanrenaud B. Intracerebroventricular administration of neuropeptide Y to normal rats increases obesegene expression in white adipose tissue. Diabetologia. 1996;39:353–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

