A molecular link between gene-specific and chromosome-wide transcriptional repression
- PMID: 11937488
- PMCID: PMC186330
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.972702
A molecular link between gene-specific and chromosome-wide transcriptional repression
Abstract
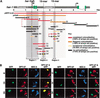
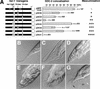
Gene-specific and chromosome-wide mechanisms of transcriptional regulation control development in multicellular organisms. SDC-2, the determinant of hermaphrodite fate in Caenorhabditis elegans, is a paradigm for both modes of regulation. SDC-2 represses transcription of X chromosomes to achieve dosage compensation, and it also represses the male sex-determination gene her-1 to elicit hermaphrodite differentiation. We show here that SDC-2 recruits the entire dosage compensation complex to her-1, directing this X-chromosome repression machinery to silence an individual, autosomal gene. Functional dissection of her-1 in vivo revealed DNA recognition elements required for SDC-2 binding, recruitment of the dosage compensation complex, and transcriptional repression. Elements within her-1 differed in location, sequence, and strength of repression, implying that the dosage compensation complex may regulate transcription along the X chromosome using diverse recognition elements that play distinct roles in repression.
Figures

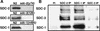

References
-
- Aparicio OM, Billington BL, Gottschling DE. Modifiers of position effect are shared between telomeric and silent mating-type loci in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991;66:1279–1287. - PubMed
-
- Carmi I, Kopczynski JB, Meyer BJ. The nuclear hormone receptor SEX-1 is an X-chromosome signal that determines nematode sex. Nature. 1998;396:168–173. - PubMed
-
- Chuang P-T, Lieb JD, Meyer BJ. Sex-specific assembly of a dosage compensation complex on the nematode X chromosome. Science. 1996;274:1736–1739. - PubMed
-
- Davis TL, Meyer BJ. SDC-3 coordinates the assembly of a dosage compensation complex on the nematode X chromosome. Development. 1997;124:1019–1031. - PubMed
-
- Dawes HE, Berlin DS, Lapidus DM, Nusbaum C, Davis TL, Meyer BJ. Dosage compensation proteins targeted to X chromosomes by a determinant of hermaphrodite fate. Science. 1999;284:1800–1804. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
