Constitutive expression of c-FLIP in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells
- PMID: 11943736
- PMCID: PMC1867202
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62578-3
Constitutive expression of c-FLIP in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells
Abstract
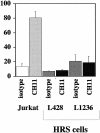
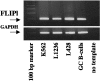
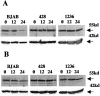
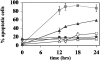
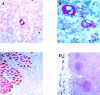
Crosslinking of the transmembrane receptor CD95/Fas leads to activation of a signaling cascade resulting in apoptosis. c-FLIP is a recently described protein that potently inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis and has been shown to be a key factor in germinal center B cell survival. Because Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells in classical Hodgkin's disease (cHD) are also resistant to Fas-mediated apoptosis we studied the role of c-FLIP in classical HD. High levels of c-FLIP protein were identified in two Fas-resistant Hodgkin-derived cell lines. In contrast to other tumor cells, inhibition of protein synthesis by cycloheximide did not lead to down-regulation of c-FLIP protein in these HD cell lines. Furthermore, Fas-mediated apoptosis was only partially restored suggesting that normal regulation of c-FLIP was disrupted. The in vivo relevance of these findings was supported by demonstration of significant c-FLIP expression by immunohistochemistry in 18 of 19 evaluable cases of primary HD. Taken together, c-FLIP is constitutively expressed in HD and may therefore be a major mechanism responsible for Fas-resistance in HD.
Figures

References
-
- Nagata S, Golstein P: The Fas death factor. Science 1995, 267:1449-1456 - PubMed
-
- Muzio M, Chinnaiyan AM, Kischkel FC, O’Rourke K, Shevchenko ANJ, Scaffidi C, Bretz JD, Zhang M, Gentz R, Mann M, Krammer PH, Peter ME, Dixit VM: FLICE, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death-inducing signaling complex. Cell 1996, 85:817-827 - PubMed
-
- Fisher GH, Rosenberg FJ, Straus SE, Dale JK, Middelton LA, Lin AY, Strober W, Lenardo MJ, Puck JM: Dominant interfering Fas gene mutations impair apoptosis in a human autoimmune lymphoproliferative disorder. Cell 1995, 81:935-946 - PubMed
-
- Drappa J, Vaishnaw AK, Sullivan KE, Chu JL, Elkon KB: Fas gene mutations in the Canale-Smith syndrome, an inherited lymphoproliferative disorder associated with autoimmunity. N Engl J Med 1996, 335:1643-1649 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

