Characteristics of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) ligand induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells
- PMID: 11950812
- PMCID: PMC1773196
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.50.5.658
Characteristics of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) ligand induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Involvement of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) in the growth response of colon cancer cells has been suggested.
Aims: To investigate the characteristics of PPARgamma induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells.
Methods: The effects of ligands for each of the PPAR subtypes (alpha, delta, and gamma) on DNA synthesis and cell viability were examined in HT-29 colon cancer cells. Modulation of apoptosis related gene expression by PPARgamma ligands was screened with cDNA arrays, and the results were confirmed by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis.
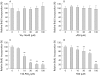
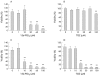
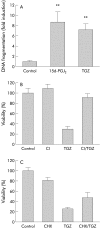
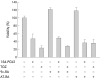
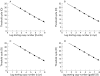
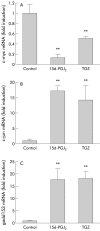
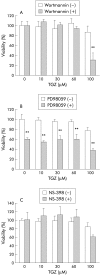
Results: PPARalpha, PPARdelta, and PPARgamma were all expressed in HT-29 cells. PPARgamma ligands, 15-deoxy-delta(12,)(14)-prostaglandin J2 (15d-PGJ2) and troglitazone (TGZ), suppressed DNA synthesis of HT-29 cells whereas ligands for PPARalpha and PPARdelta had no significant effects. Both 15d-PGJ2 and TGZ induced HT-29 cell death in a dose dependent manner which was associated with an increase in fragmented DNA and was sensitive to a caspase inhibitor. Among several genes selected by cDNA array screening, quantitative RT-PCR analysis confirmed downregulation of c-myc expression and upregulation of c-jun and gadd153 expression by 15d-PGJ2 and TGZ. PPARgamma induced apoptosis was antagonised by the presence of serum in the culture medium, and interaction between PPARgamma signalling and cell survival signalling through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway was suggested.
Conclusions: As c-myc is an important target gene of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC)/beta-catenin and/or APC/gamma-catenin pathway, activation of PPARgamma signalling appears to compensate for deregulated c-myc expression caused by mutated APC. The present results suggest the potential usefulness of PPARgamma ligands for chemoprevention and treatment of colon cancers.
Figures
Comment in
-
[PPAR-ligands: a clinically important regulatory system with multiple options in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, inflammatory bowel disease and in the chemoprevention of colon cancer?].Z Gastroenterol. 2003 Oct;41(10):1035-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-42921. Z Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 14562202 German. No abstract available.
References
-
- Vamecq J, Latruffe N. Medical significance of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Lancet 1999;354:141–8. - PubMed
-
- Tontonoz P, Hu E, Spiegelman BM. Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPAR gamma 2, a lipid-activated transcription factor. Cell 1994;79:1147–56. - PubMed
-
- Forman BM, Tontonoz P, Chen J, et al. 15-Deoxy-delta 12, 14-prostaglandin J2 is a ligand for the adipocyte determination factor PPAR gamma. Cell 1995;83:803–12. - PubMed
-
- Kliewer SA, Lenhard JM, Willson TM, et al. A prostaglandin J2 metabolite binds peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and promotes adipocyte differentiation. Cell 1995;83:813–19. - PubMed
-
- Mansen A, Guardiola-Diaz H, Rafter J, et al. Expression of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) in the mouse colonic mucosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996;222:844–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
