Cyclooxygenase inhibition: between the devil and the deep blue sea
- PMID: 11953329
- PMCID: PMC1867681
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.50.suppl_3.iii25
Cyclooxygenase inhibition: between the devil and the deep blue sea
Abstract
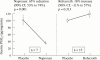
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) account for more reports of drug related toxicity than any other class of drugs. Their most widely recognised adverse effects are on the gastrointestinal tract. They cause acute erosions and chronic ulcers that result in hospitalisation and death because of ulcer bleeding and perforation. Between them, aspirin and non-aspirin NSAIDs may account for more than half of all episodes of ulcer bleeding and perforation.
Figures

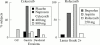


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
