Identification and characterization of the ESAT-6 homologue of Mycobacterium leprae and T-cell cross-reactivity with Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 11953394
- PMCID: PMC127910
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.5.2544-2548.2002
Identification and characterization of the ESAT-6 homologue of Mycobacterium leprae and T-cell cross-reactivity with Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
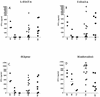
In this paper we describe identification and characterization of Mycobacterium leprae ESAT-6 (L-ESAT-6), the homologue of M. tuberculosis ESAT-6 (T-ESAT-6). T-ESAT-6 is expressed by all pathogenic strains belonging to the M. tuberculosis complex but is absent from virtually all other mycobacterial species, and it is a promising antigen for immunodiagnosis of tuberculosis (TB). Therefore, we analyzed whether L-ESAT-6 is a similarly powerful tool for the study of leprosy by examining T-cell responses against L-ESAT-6 in leprosy patients, TB patients, and exposed or nonexposed healthy controls from areas where leprosy and TB are endemic and areas where they are not endemic. L-ESAT-6 was recognized by T cells from leprosy patients, TB patients, individuals who had contact with TB patients, and healthy individuals from an area where TB and leprosy are endemic but not by T cells from individuals who were not exposed to M. tuberculosis and M. leprae. Moreover, leprosy patients who were not responsive to M. leprae failed to respond to L-ESAT-6. A very similar pattern was obtained with T-ESAT-6. These results show that L-ESAT-6 is a potent M. leprae antigen that stimulates T-cell-dependent gamma interferon production in a large proportion of individuals exposed to M. leprae. Moreover, our results suggest that there is significant cross-reactivity between T-ESAT-6 and L-ESAT-6, which has implications for the use of ESAT-6 as tool for diagnosis of leprosy and TB in areas where both diseases are endemic.
Figures


Comment in
-
ESAT-6 and CFP-10: what is the diagnosis?Infect Immun. 2002 Nov;70(11):6509-10; author reply 6511. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.11.6509-6511.2002-a. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12379740 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Andersen, P. 1994. The T cell response to secreted antigens of M. tuberculosis. Immunobiology 191:537-547. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, P., A. B. Andersen, A. L. Sorensen, and S. Nagai. 1995. Recall of long-lived immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in mice. J. Immunol. 154:3359-3372. - PubMed
-
- Arend, S. M., P. Andersen, K. E. van Meijgaarden, R. L. V. Skjøt, J. T. van Dissel, and T. H. M. Ottenhoff. 2000. Detection of active tuberculosis infection by T cell responses to early secreted antigen target 6 kDa protein and culture filtrate protein 10. J. Infect. Dis. 181:1850-1854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

