The LIM-homeodomain transcription factor Lmx1b plays a crucial role in podocytes
- PMID: 11956245
- PMCID: PMC150943
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI13961
The LIM-homeodomain transcription factor Lmx1b plays a crucial role in podocytes
Abstract
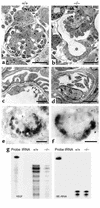
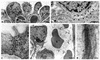
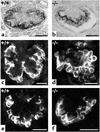
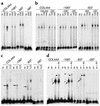
Patients with nail-patella syndrome often suffer from a nephropathy, which ultimately results in chronic renal failure. The finding that this disease is caused by mutations in the transcription factor LMX1B, which in the kidney is expressed exclusively in podocytes, offers the opportunity for a better understanding of the renal pathogenesis. In our analysis of the nephropathy in nail-patella syndrome, we have made use of the Lmx1b knockout mouse. Transmission electron micrographs showed that glomerular development in general and the differentiation of podocytes in particular were severely impaired. The glomerular capillary network was poorly elaborated, fenestrae in the endothelial cells were largely missing, and the glomerular basement membrane was split. In addition podocytes retained a cuboidal shape and did not form foot processes and slit diaphragms. Expression of the alpha4 chain of collagen IV and of podocin was also severely reduced. Using gel shift assays, we demonstrated that LMX1B bound to two AT-rich sequences in the promoter region of NPHS2, the gene encoding podocin. Our results demonstrate that Lmx1b regulates important steps in glomerular development and establish a link between three hereditary kidney diseases: nail-patella syndrome (Lmx1b), steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (podocin), and Alport syndrome (collagen IV alpha4).
Figures


References
-
- Bennett WM, et al. The nephropathy of the nail-patella syndrome. Clinicopathologic analysis of 11 kindred. Am J Med. 1973;54:304–319. - PubMed
-
- del Pozo E, Lapp H. Ultrastructure of the kidney in the nephropathy of the nail-patella syndrome. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970;54:845–851. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Bassat M, Cohen L, Rosenfeld J. The glomerular basement membrane in the nail-patella syndrome. Arch Pathol. 1971;92:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Drut RM, Chandra S, Latorraca R, Gilbert-Barness E. Nail-patella syndrome in a spontaneously aborted 18-week fetus: ultrastructural and immunofluorescent study of the kidneys. Am J Med Genet. 1992;43:693–696. - PubMed
-
- Lubec B, Arbeiter K, Ulrich W, Frauscher G. Hereditary osteo-onycho-renal dysplasia with excess urinary pyridinoline cross-links and abnormal kidney collagen cross-linking. Nephron. 1995;70:255–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

