Characterization of plasmids carrying CMY-2 from expanded-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant Salmonella strains isolated in the United States between 1996 and 1998
- PMID: 11959555
- PMCID: PMC127137
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.5.1269-1272.2002
Characterization of plasmids carrying CMY-2 from expanded-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant Salmonella strains isolated in the United States between 1996 and 1998
Abstract
Sequencing of DNA from 15 expanded-spectrum cephalosporin (e.g., ceftriaxone)-resistant Salmonella isolates obtained in the United States revealed that resistance to ceftriaxone in all isolates was mediated by cmy-2. Hybridization patterns revealed three plasmid structures containing cmy-2 in these 15 isolates. These data suggest that the spread of cmy-2 among Salmonella strains is occurring through mobilization of the cmy-2 gene into different plasmid backbones and consequent horizontal transfer by conjugation.
Figures
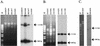
References
-
- Angulo, F. J., K. R. Johnson, R. V. Tauxe, and M. L. Cohen. 2000. Origins and consequences of antimicrobial-resistant nontyphoidal Salmonella: implications for the use of fluoroquinolones in food animals. Microb. Drug Resist. 6:77-83. - PubMed
-
- Bachman, B. 1987. Derivations and genotypes of some mutant derivatives of Escherichia coli K-12, p. 1190-1219. In F. C. Niedhardt, J. L. Ingraham, K. B. Low, B. Magasanik, M. Schaechter, and H. E. Umbarger (ed.), Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology, vol. 1. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

