New Mg2+-dependent oxytetracycline resistance determinant tet 34 in Vibrio isolates from marine fish intestinal contents
- PMID: 11959596
- PMCID: PMC127156
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.5.1550-1552.2002
New Mg2+-dependent oxytetracycline resistance determinant tet 34 in Vibrio isolates from marine fish intestinal contents
Abstract
A new oxytetracycline (OTC) resistance (Otc(r)) determinant, Tet 34, was cloned from chromosomal DNA of Vibrio sp. no. 6 isolated from intestinal contents of cultured yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata). The transformant, containing cloned Tet 34, could grow in broth containing 25 microg of drug per ml with 10 mM MgCl2. Tet 34 encoded an open reading frame (ORF) 154 amino acids long. The amino acid sequence of the ORF was homologous to sequences of several bacterial xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferases (XPRTs), which act in purine nucleotide salvage synthesis. Mg2+ binding site residues and the active site were highly conserved in XPRT and the ORF of Tet 34. The results suggest that Tet 34 encodes a new Mg2+-dependent Otc(r) mechanism.
Figures
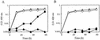

References
-
- Chopra, I., P. M. Hawkey, and M. Hinton. 1992. Tetracyclines, molecular and clinical aspects. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 29:245-277. - PubMed
-
- DePaola, A., P. A. Flynn, R. M. McPhearson, and S. B. Levy. 1988. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of tetracycline- and oxytetracycline-resistant Aeromonas hydrophila from cultured channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) and their environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54:1861-1863. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

