Gemifloxacin is efficacious against penicillin-resistant and quinolone-resistant pneumococci in experimental meningitis
- PMID: 11959614
- PMCID: PMC127126
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.5.1607-1609.2002
Gemifloxacin is efficacious against penicillin-resistant and quinolone-resistant pneumococci in experimental meningitis
Abstract
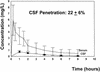
In experimental rabbit meningitis, gemifloxacin penetrated inflamed meninges well (22 to 33%) and produced excellent bactericidal activity (change in log(10) [Deltalog(10)] CFU/ml/h, -0.68 +/- 0.30 [mean and standard deviation]), even superior to that of the standard regimen of ceftriaxone plus vancomycin (-0.49 +/- 0.09 deltalog(10) CFU/ml/h), in the treatment of meningitis due to a penicillin-resistant pneumococcal strain (MIC, 4 mg/liter). Even against a penicillin- and quinolone-resistant strain, gemifloxacin showed good bactericidal activity (-0.48 +/- 0.16 deltalog(10) CFU/ml/h). The excellent antibacterial activity of gemifloxacin was also confirmed by time-kill assays over 8 h in vitro.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacies of BMS 284756 against penicillin-sensitive, penicillin-resistant, and quinolone-resistant pneumococci in experimental meningitis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Jan;46(1):184-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.1.184-187.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 11751131 Free PMC article.
-
Gemifloxacin is effective in experimental pneumococcal meningitis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000 Mar;44(3):767-70. doi: 10.1128/AAC.44.3.767-770.2000. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000. PMID: 10681354 Free PMC article.
-
Synergy between trovafloxacin and ceftriaxone against penicillin-resistant pneumococci in the rabbit meningitis model and in vitro.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000 Aug;44(8):2179-81. doi: 10.1128/AAC.44.8.2179-2181.2000. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000. PMID: 10898696 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacodynamics to combat resistance.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2000 Jul;46 Suppl T1:25-31. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jac.a020890. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2000. PMID: 10997596 Review.
-
Gemifloxacin: survival of the fittest.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2000 Jul;46 Suppl T1:33-7. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jac.a020892. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2000. PMID: 10997597 Review.
Cited by
-
Fluoroquinolones in the Treatment of Meningitis.Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2003 Aug;5(4):329-336. doi: 10.1007/s11908-003-0011-0. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2003. PMID: 12866985
-
Biochemical Characterization of New Gemifloxacin Schiff Base (GMFX-o-phdn) Metal Complexes and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial Activity against Some Phyto- or Human Pathogens.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 14;23(4):2110. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042110. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216223 Free PMC article.
-
Structural, Spectroscopic, and Docking Analysis of N,O-Donor Ligand Metal Complex Nanoparticles With Hypolipidemic Effects via Lipoprotein Lipase Activation in High-Fat Diet Mice.Chem Biodivers. 2025 May;22(5):e202403003. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202403003. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 39671531 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed, A. 1997. A critical evaluation of vancomycin for treatment of bacterial meningitis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 16:895-903 - PubMed
-
- Bradley, J., and W. M. Scheld. 1997. Penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis: current antibiotic therapy in the 1990s. Clin. Infect. Dis. 24(Suppl.):213-221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

