A DNA vector-based RNAi technology to suppress gene expression in mammalian cells
- PMID: 11960009
- PMCID: PMC122801
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.082117599
A DNA vector-based RNAi technology to suppress gene expression in mammalian cells
Abstract
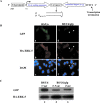
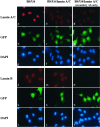
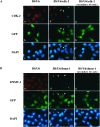
Double-stranded RNA-mediated interference (RNAi) has recently emerged as a powerful reverse genetic tool to silence gene expression in multiple organisms including plants, Caenorhabditis elegans, and Drosophila. The discovery that synthetic double-stranded, 21-nt small interfering RNA triggers gene-specific silencing in mammalian cells has further expanded the utility of RNAi into mammalian systems. Here we report a technology that allows synthesis of small interfering RNAs from DNA templates in vivo to efficiently inhibit endogenous gene expression. Significantly, we were able to use this approach to demonstrate, in multiple cell lines, robust inhibition of several endogenous genes of diverse functions. These findings highlight the general utility of this DNA vector-based RNAi technology in suppressing gene expression in mammalian cells.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

