Localization of caveolin 1 in aortic valve endothelial cells using antigen retrieval
- PMID: 11967273
- PMCID: PMC3951858
- DOI: 10.1177/002215540205000503
Localization of caveolin 1 in aortic valve endothelial cells using antigen retrieval
Abstract
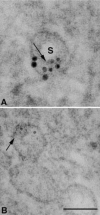
Ultrastructural analysis of aortic valve endothelial cells subjected to growth arrest revealed many vesicles defined as caveolae by the localization of caveolin. Translocation of caveolin after exposure to oxidized LDL suggests that the localization of caveolin may be a valuable tool to study models of early atherogenesis. In this study, several antigen retrieval protocols were tested in osmium-fixed and Spurr-embedded cells to determine the optimal method of antigen retrieval in our model system. SDS produced the most consistent labeling pattern. A quantitative evaluation revealed that SDS significantly increased the labeling density in Spurr-embedded cells. The labeling pattern appeared as clusters of gold particles, 15-40 nm in diameter, that were associated with membranes of a similar size which may represent the neck region of the caveolae.
Figures






References
-
- Amino K, Honda Y, Ide C, Fujimoto T. Distribution of plasmalemmal Ca(2+)-pump and caveolin in the corneal epithelium during the wound healing process. Curr Eye Res. 1997;16:1088–1095. - PubMed
-
- Bendayan M, Zollinger M. Ultrastructural localization of antigenic sites on osmium-fixed tissues applying the protein A-gold technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983;31:101–109. - PubMed
-
- Blair A, Shaul PW, Yahanna IS, Conrad PA, Smart EJ. Oxidized low density lipoprotein displaces endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS) from plasmalemmal caveolae and impairs eNOS activation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:32512–32519. - PubMed
-
- Brorson SH. Fixative-dependent increase in immunogold labeling following antigen retrieval on acrylic and epoxy sections. Biotech Histochem. 1999;74:248–260. - PubMed
-
- Brown D, Lydon J, McLaughlin M, Stuart–Tilley A, Tyszkowski R, Alper S. Antigen retrieval in cryostat sections and cultured cells by treatment with sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) Histochem Cell Biol. 1996;105:261–267. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

