The CD40-TRAF6 axis controls affinity maturation and the generation of long-lived plasma cells
- PMID: 11967542
- PMCID: PMC2834483
- DOI: 10.1038/ni792
The CD40-TRAF6 axis controls affinity maturation and the generation of long-lived plasma cells
Abstract
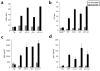
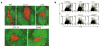
Affinity maturation of the immune response and the generation of long-lived bone marrow (BM) plasma cells are hallmarks of CD40-dependent, thymus-dependent (TD) humoral immunity. Through disruption of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-associated factor 6 (TRAF6)-binding site within the CD40 cytoplasmic domain, we selectively ablated affinity maturation and the generation of plasma cells after immunization. Mutagenesis of both the TRAF6 and TRAF2-TRAF3 sites was essential for arresting germinal center formation in response to immunization. CD40-induced B cell proliferation and early immunoglobulin production occurred even when all TRAF sites were ablated. These studies show that specific CD40-TRAF associations control well defined aspects of humoral immunity. In addition, they define the roles that TRAF-dependent and TRAF-independent pathways play in regulating antigen-driven B cell differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement: The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures


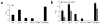
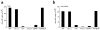
References
-
- Banchereau J, et al. The CD40 antigen and its ligand. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:881–922. - PubMed
-
- Pullen SS, et al. CD40-tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) interactions: regulation of CD40 signaling through multiple TRAF binding sites and TRAF hetero-oligomerization. Biochemistry. 1998;37:11836–11845. - PubMed
-
- Pullen SS, Dang TT, Crute JJ, Kehry MR. CD40 signaling through tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs). Binding site specificity and activation of downstream pathways by distinct TRAFs. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:14246–14254. - PubMed
-
- Cheng G, Baltimore D. TANK, a co-inducer with TRAF2 of TNF- and CD 40L-mediated NF-κB activation. Genes Dev. 1996;10:963–973. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

