Kinetics and mechanism of the DNA double helix invasion by pseudocomplementary peptide nucleic acids
- PMID: 11972051
- PMCID: PMC122883
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.092127999
Kinetics and mechanism of the DNA double helix invasion by pseudocomplementary peptide nucleic acids
Abstract
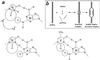
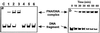
If adenines and thymines in two mutually complementary mixed-base peptide nucleic acid (PNA) oligomers are substituted with diaminopurines and thiouracils, respectively, so-called pseudocomplementary PNAs (pcPNAs) are created. Pairs of pcPNAs have recently demonstrated an ability to highly selectively target essentially any designated site on double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) by forming very stable PNA-DNA strand-displacement complexes via double duplex invasion (helix invasion). These properties of pcPNAs make them unique and very promising ligands capable of denying the access of DNA-binding proteins to dsDNA. To elucidate the sequence-unrestricted mechanism of sequence-specific dsDNA recognition by pcPNAs, we have studied the kinetics of formation of corresponding PNA-DNA complexes at various temperatures by the gel-shift assay. In parallel, the conditions for possible self-hybridization of pcPNA oligomers have been assayed by mixing curve (Job plot) and thermal melting experiments. The data indicate that, at physiological temperatures ( approximately 37 degrees C), the equilibrium is shifted toward the pairing of corresponding pcPNAs with each other. This finding explains a linear concentration dependence, within the submicromolar range, of the pcPNA invasion rate into dsDNA at 37 degrees C. At elevated temperatures (>50 degrees C), the rather unstable pcPNA duplexes dissociate, yielding the expected quadratic dependence for the rate of pcPNA invasion on the PNA concentration. The polycationic character of pcPNA pairs, carrying the duplicated number of protonated terminal PNA residues commonly used to increase the PNA solubility and binding affinity, also explains the self-inhibition of pcPNA invasion observed at higher PNA concentrations. Melting of pcPNA duplexes occurs with the integral transition enthalpies ranged from -235 to -280 kJ.mol(-1), contributing to an anomalously high activation energy of approximately 150 kJ.mol(-1) found for the helix invasion of pcPNAs carrying four different nucleobases. A simplified kinetic model for pcPNAs helix invasion is proposed that interprets all unusual features of pcPNAs binding to dsDNA. Our findings have important implications for rational use of pcPNAs.
Figures


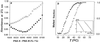
Similar articles
-
Sequence-specific protection of duplex DNA against restriction and methylation enzymes by pseudocomplementary PNAs.Biochemistry. 2000 Sep 5;39(35):10908-13. doi: 10.1021/bi000675e. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10978178
-
Origin of high fidelity in target-sequence recognition by PNA-Ce(IV)/EDTA combinations as site-selective DNA cutters.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Feb 25;131(7):2657-62. doi: 10.1021/ja808290e. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19199631
-
Pseudocomplementary PNAs as selective modifiers of protein activity on duplex DNA: the case of type IIs restriction enzymes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jul 15;31(14):3929-35. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg450. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12853608 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition Mechanisms and Applications of Peptide Nucleic Acids Targeting Double-stranded DNA.Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(41):4681-4705. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666161028154243. Curr Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27915983 Review.
-
Applications of PNA-Based Artificial Restriction DNA Cutters.Molecules. 2017 Sep 21;22(10):1586. doi: 10.3390/molecules22101586. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28934140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pseudo-complementary PNA actuators as reversible switches in dynamic DNA nanotechnology.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Apr;41(8):4729-39. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt121. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23444144 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Peptide Nucleic Acids-Facts and Perspectives.Molecules. 2020 Jan 28;25(3):559. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030559. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32012929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyrrolidinyl peptide nucleic acid with α/β-peptide backbone: A conformationally constrained PNA with unusual hybridization properties.Artif DNA PNA XNA. 2011 Apr;2(2):50-59. doi: 10.4161/adna.2.2.16340. Artif DNA PNA XNA. 2011. PMID: 21912727 Free PMC article.
-
RecA-mediated strand invasion of DNA by oligonucleotides substituted with 2-aminoadenine and 2-thiothymine.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Dec;36(21):6806-15. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn755. Epub 2008 Oct 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18953036 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated photobleaching of a cyanine dye in the presence of a ternary target DNA, PNA probe, dye catalytic complex: a molecular diagnostic.Anal Chem. 2009 Mar 15;81(6):2043-52. doi: 10.1021/ac702519k. Anal Chem. 2009. PMID: 19231844 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nielsen P E, Egholm M, Berg R H, Buchardt O. Science. 1991;254:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Uhlmann E, Peyman A, Breipohl G, Will D W. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1998;37:2796–2823. - PubMed
-
- Falkiewicz B. Acta Biochim Polon. 1999;46:509–529. - PubMed
-
- Winters T A. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2000;2:670–681. - PubMed
-
- Ganesh K N, Nielsen P E. Curr Org Chem. 2000;4:916–928.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

