Staphylococcal enterotoxin H contrasts closely related enterotoxins in species reactivity
- PMID: 11972634
- PMCID: PMC1782703
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2002.01409.x
Staphylococcal enterotoxin H contrasts closely related enterotoxins in species reactivity
Abstract
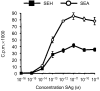
Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin H (SEH) belongs to the staphylococcal enterotoxin (SE) family of superantigens (SAgs). SEH has structural similarities to other SE; however, its biological properties are less well characterized. SEH binds with high affinity to human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II and exhibits strong mitogenic activity in human T cells, although it was found to be less potent than the related SEA. Surprisingly and in sharp contrast to related SEs, SEH did not possess superantigen activity in murine T cells and T cells from three investigated rat strains. However, SEH bound to a high extent to murine MHC class II expressing cells and when presented by these cells SEH stimulated human T cells to proliferate. Thus, SEH interacts with the murine MHC class II molecule in a functional manner. Notably, SEH had an inhibitory effect on murine SEA response, demonstrating that SEH interferes with the SEA interactions with murine cells. Despite this, murine T cells did not proliferate regardless of whether SEH was presented on human or murine MHC class II expressing cells. Consequently, SEH differs in species reactivity as compared to related SEs and lacks critical properties for T-cell activation in mice. We propose that unlike other SEs, SEH does not interact with murine T cells since it is not recognized by murine T-cell receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The crystal structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin H: implications for binding properties to MHC class II and TcR molecules.J Mol Biol. 2000 Sep 22;302(3):527-37. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4093. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10986116
-
Staphylococcal enterotoxin H displays unique MHC class II-binding properties.J Immunol. 1999 Dec 15;163(12):6686-93. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10586065
-
Superantigenic staphylococcal exotoxins induce T-cell proliferation in the presence of Langerhans cells or class II-bearing keratinocytes and stimulate keratinocytes to produce T-cell-activating cytokines.J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Jan;102(1):31-8. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12371727. J Invest Dermatol. 1994. PMID: 8288908
-
Staphylococcal enterotoxin microbial superantigens.FASEB J. 1991 Sep;5(12):2706-12. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.12.1916093. FASEB J. 1991. PMID: 1916093 Review.
-
Superantigens: interaction of staphylococcal enterotoxins with MHC class II molecules.Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1990;101:195-204; discussion 204-6. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1990. PMID: 2577245 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Two common structural motifs for TCR recognition by staphylococcal enterotoxins.Sci Rep. 2016 May 16;6:25796. doi: 10.1038/srep25796. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27180909 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of emetic response to staphylococcal enterotoxins in the house musk shrew (Suncus murinus).Infect Immun. 2003 Jan;71(1):567-70. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.1.567-570.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12496213 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization of Equine Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Exhibiting Reduced Oxacillin Susceptibility.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Sep 13;11(9):535. doi: 10.3390/toxins11090535. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31540335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fraser J, Arcus V, Kong P, Baker E, Proft T. Superantigens – powerful modifiers of the immune system. Mol Med Today. 2000;6:125–32. - PubMed
-
- Lavoie PM, Thibodeau J, Erard F, Sekaly RP. Understanding the mechanism of action of bacterial superantigens from a decade of research. Immunol Rev. 1999;168:257–69. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

