AerR, a second aerobic repressor of photosynthesis gene expression in Rhodobacter capsulatus
- PMID: 11976310
- PMCID: PMC135018
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.10.2805-2814.2002
AerR, a second aerobic repressor of photosynthesis gene expression in Rhodobacter capsulatus
Abstract
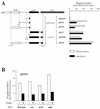
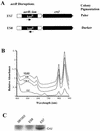
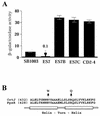
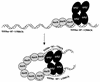
Open reading frame orf192, which is located immediately upstream of the aerobic repressor gene crtJ, was genetically and biochemically demonstrated to code for a second aerobic repressor (AerR) of photosynthesis gene expression in Rhodobacter capsulatus. Promoter-mapping studies indicate that crtJ has its own promoter but that a significant proportion of crtJ expression is promoted by read-through transcription of orf192 (aerR) transcripts through crtJ. Disruption of aerR resulted in increased photopigment biosynthesis during aerobic growth to a level similar to that of disruption of crtJ. Like that reported for CrtJ, beta-galactosidase assays of reporter gene expression indicated that disruption of aerR resulted in a two- to threefold increase in aerobic expression of the crtI and pucB operons. However, unlike CrtJ, AerR aerobically represses puf operon expression and does not aerobically repress bchC expression. Gel mobility shift analysis with purified AerR indicates that AerR does not bind to a bchC promoter probe but does bind to the crtI, puc, and puf promoter probes. These results indicate that AerR is a DNA-binding protein that targets genes partially overlapping a subset of genes that are also controlled by CrtJ. We also provide evidence for cooperative binding of AerR and CrtJ to the puc promoter region.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The tetrapyrrole biosynthetic pathway and its regulation in Rhodobacter capsulatus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;675:229-50. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-1528-3_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20532744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Vitamin B12-Dependent Photoreceptor AerR Relieves Photosystem Gene Repression by Extending the Interaction of CrtJ with Photosystem Promoters.mBio. 2017 Mar 21;8(2):e00261-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00261-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28325764 Free PMC article.
-
CrtJ bound to distant binding sites interacts cooperatively to aerobically repress photopigment biosynthesis and light harvesting II gene expression in Rhodobacter capsulatus.J Biol Chem. 1998 Nov 13;273(46):30762-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.46.30762. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9804853
-
Vitamin B12 regulates photosystem gene expression via the CrtJ antirepressor AerR in Rhodobacter capsulatus.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Feb;91(4):649-64. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12491. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24329562 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen-regulated expression of genes for pigment binding proteins in Rhodobacter capsulatus.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002 May;4(3):249-53. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 11931555 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Photosystem Synthesis in Rhodobacter capsulatus.Photosynth Res. 2004;80(1-3):353-60. doi: 10.1023/B:PRES.0000030440.99968.68. Photosynth Res. 2004. PMID: 16328832
-
The tetrapyrrole biosynthetic pathway and its regulation in Rhodobacter capsulatus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;675:229-50. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-1528-3_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20532744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The blue light-dependent LOV-protein LdaP of Dinoroseobacter shibae acts as antirepressor of the PpsR repressor, regulating photosynthetic gene cluster expression.Front Microbiol. 2024 Feb 7;15:1351297. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1351297. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38404597 Free PMC article.
-
RegB/RegA, a highly conserved redox-responding global two-component regulatory system.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004 Jun;68(2):263-79. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.68.2.263-279.2004. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15187184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activity of the tetrapyrrole regulator CrtJ is controlled by oxidation of a redox active cysteine located in the DNA binding domain.Mol Microbiol. 2012 Aug;85(4):734-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08135.x. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Mol Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22715852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberti, M., D. H. Burke, and J. E. Hearst. 1995. Structure and sequence of the photosynthesis gene cluster, p. 1083-1106. In R. E. Blankenship, M. T. Madigan, and C. E. Bauer (ed.), Anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
-
- Alexeyev, M. F. 1995. Three kanamycin resistance gene cassettes with different polylinkers. BioTechniques 18:52-56. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, C. E., and T. H. Bird. 1996. Regulatory circuits controlling photosynthesis gene expression. Cell 85:5-8. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, C. E., D. A. Young, and B. L. Marrs. 1988. Analysis of the Rhodobacter capsulatus puf operon. Location of the oxygen-regulated promoter region and the identification of an additional puf-encoded gene. J. Biol. Chem. 263:4820-4827. - PubMed
-
- Bollivar, D. W., J. Y. Suzuki, J. T. Beatty, J. M. Dobrowolski, and C. E. Bauer. 1994. Directed mutational analysis of bacteriochlorophyll a biosynthesis in Rhodobacter capsulatus. J. Mol. Biol. 237:622-640. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

