Characterization of the c-MYC-regulated transcriptome by SAGE: identification and analysis of c-MYC target genes
- PMID: 11983916
- PMCID: PMC122939
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.082005599
Characterization of the c-MYC-regulated transcriptome by SAGE: identification and analysis of c-MYC target genes
Abstract
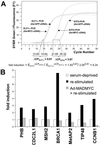
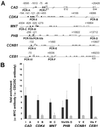
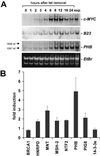
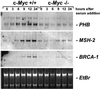
To identify target genes of the oncogenic transcription factor c-MYC, serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE) was performed after adenoviral expression of c-MYC in primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells: 216 different SAGE tags, corresponding to unique mRNAs, were induced, whereas 260 tags were repressed after c-MYC expression (P < 0.05). The induction of 53 genes was confirmed by using microarray analysis and quantitative real-time PCR: among these genes was MetAP2/p67, which encodes an activator of translational initiation and represents a validated target for inhibition of neovascularization. Furthermore, c-MYC induced the cell cycle regulatory genes CDC2-L1, Cyclin E binding protein 1, and Cyclin B1. The DNA repair genes BRCA1, MSH2, and APEX were induced by c-MYC, suggesting that c-MYC couples DNA replication to processes preserving the integrity of the genome. MNT, a MAX-binding antagonist of c-MYC function, was up-regulated, implying a negative feedback loop. In vivo promoter occupancy by c-MYC was detected by chromatin immunoprecipitation for CDK4, Prohibitin, MNT, Cyclin B1, and Cyclin E binding protein 1, showing that these genes are direct c-MYC targets. The c-MYC-regulated genes/tags identified here will help to define the set of bona fide c-MYC targets and may have potential therapeutic value for inhibition of cancer cell proliferation, tumor-vascularization, and restenosis.
Figures
Comment in
-
Disentangling the MYC web.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Apr 30;99(9):5757-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.102173199. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11983876 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Oster S K, Ho C S W, Soucie E L, Penn L Z. Adv Cancer Res. 2002;84:81–154. - PubMed
-
- Eisenman R N. Genes Dev. 2001;15:2023–2030. - PubMed
-
- Grandori C, Cowley S M, James L P, Eisenman R N. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:653–699. - PubMed
-
- Grandori C, Eisenman R N. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:177–181. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

